How to Enable Flash in Chrome: A Comprehensive Guide
Adobe Flash Player, once a ubiquitous plugin for web browsers, has largely been phased out due to security vulnerabilities and the rise of more efficient technologies like HTML5. However, there may still be instances where you need to enable Flash in Chrome to access legacy content or specific applications. This guide provides a step-by-step process on how to enable Flash in Chrome, along with important considerations about its security implications. We’ll explore the reasons behind Flash’s decline, alternative solutions, and best practices for managing Flash content if you still need it.
Understanding the Decline of Flash
Before diving into the process of how to enable Flash in Chrome, it’s crucial to understand why Flash has been deprecated. Flash Player was once essential for displaying multimedia content on the web, including videos, animations, and interactive games. However, it suffered from numerous security flaws, leading to frequent exploits and vulnerabilities. Modern web standards like HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript offer more secure and efficient alternatives for delivering rich web experiences.
Major browsers, including Chrome, have gradually reduced support for Flash, culminating in its official end-of-life in December 2020. After this date, Adobe stopped providing security updates for Flash Player, making it even more vulnerable to attacks. While you can still enable Flash in Chrome in certain situations, it’s strongly recommended to avoid doing so unless absolutely necessary.
Steps to Enable Flash in Chrome (If Absolutely Necessary)
Disclaimer: Enabling Flash Player poses security risks. Only proceed if you fully understand the potential consequences and have exhausted all other alternatives. Ensure you are visiting a trusted website before enabling Flash.
Method 1: Site-Specific Flash Activation
- Navigate to the Website: Open Chrome and go to the website that requires Flash.
- Check for Flash Blocking: Look for a puzzle piece icon or a message indicating that Flash is blocked in the address bar.
- Allow Flash: Click on the puzzle piece icon or the message. A prompt will appear asking if you want to allow Flash to run on the site.
- Select ‘Allow’: Choose the ‘Allow’ option to enable Flash in Chrome for that specific website. You may also see options like ‘Run this time’ or ‘Always allow on this site.’
- Refresh the Page: Refresh the page to load the Flash content.
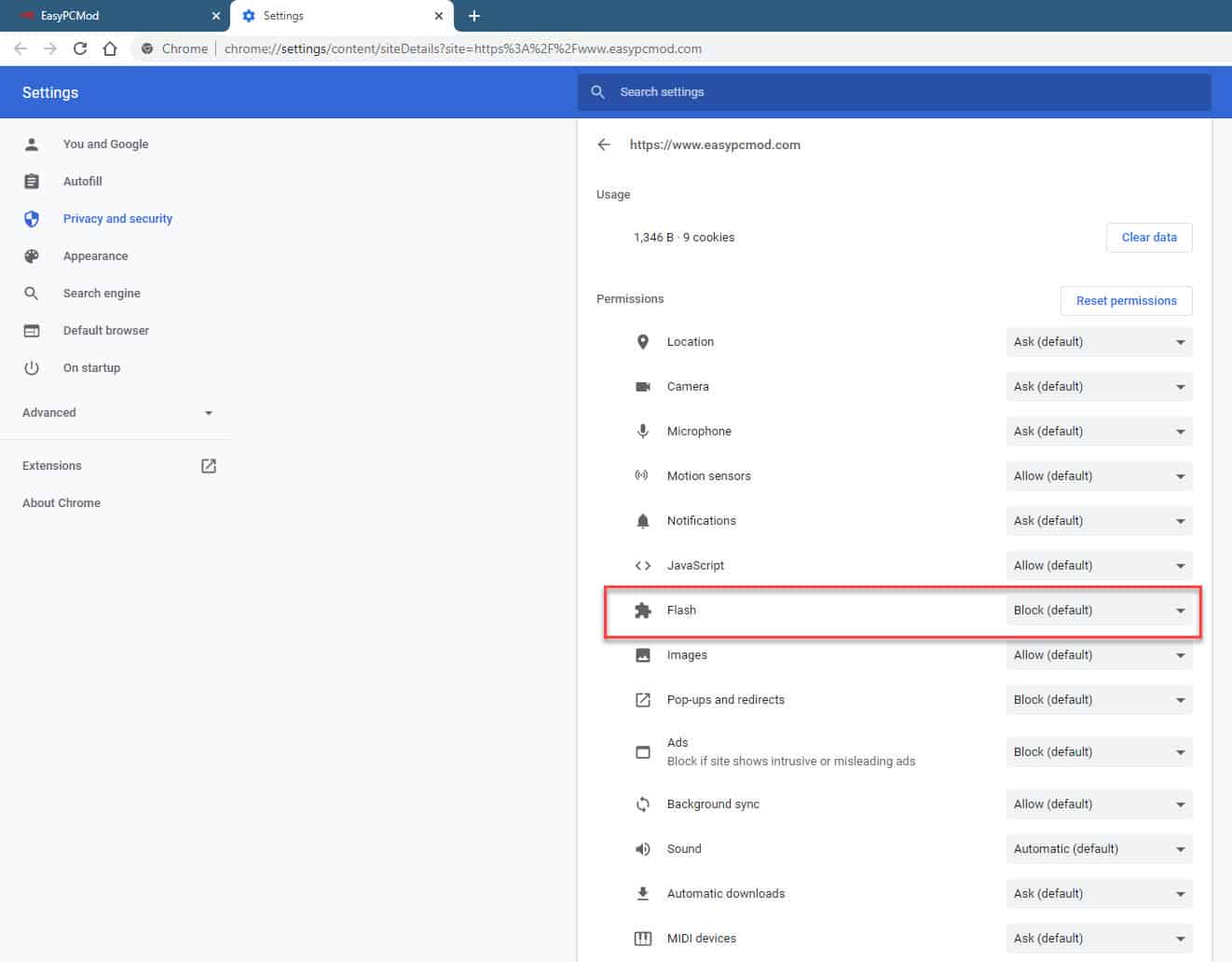
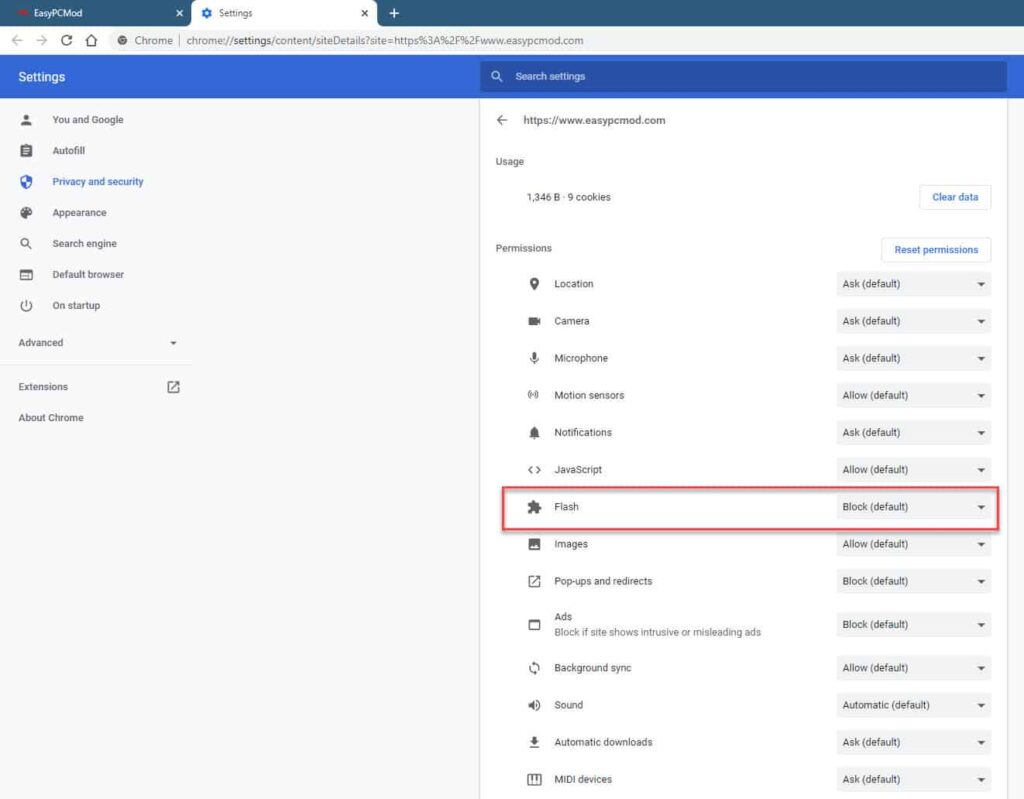
Method 2: Global Flash Settings (Not Recommended)
Warning: Enabling Flash globally is highly discouraged due to security risks. This method should only be used as a last resort and with extreme caution.
- Access Chrome Settings: In Chrome, type
chrome://settings/content/flashin the address bar and press Enter. This will take you directly to the Flash settings. Alternatively, you can go to Settings > Privacy and security > Site Settings > Flash. - Enable ‘Ask first’: Ensure that the ‘Ask first before allowing sites to run Flash (recommended)’ option is enabled. This prevents Flash from running automatically on all websites.
- Add Exceptions (If Needed): If you need to enable Flash in Chrome for specific websites, you can add them to the ‘Allow’ list. Click the ‘Add’ button and enter the URL of the website.
- Consider ‘Block sites from running Flash’: If you want to completely disable Flash, select the ‘Block sites from running Flash’ option.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after attempting to enable Flash in Chrome, you might encounter issues. Here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Check Flash Player Installation: Ensure that Adobe Flash Player is installed on your computer. If not, download and install it from the official Adobe website (use caution and verify the source).
- Update Chrome: Make sure you’re using the latest version of Chrome. Outdated browser versions might have compatibility issues.
- Clear Cache and Cookies: Clearing your browser’s cache and cookies can resolve conflicts and ensure that the website loads correctly.
- Disable Extensions: Browser extensions can sometimes interfere with Flash Player. Try disabling extensions one by one to identify any conflicts.
- Check Firewall/Antivirus: Your firewall or antivirus software might be blocking Flash Player. Check their settings to ensure that Flash is allowed.
- Verify Website Compatibility: Confirm that the website actually requires Flash. Some websites might incorrectly display a Flash error message even if they use other technologies.
Security Considerations
As mentioned earlier, enabling Flash poses significant security risks. Here are some best practices to minimize those risks:
- Only Enable Flash When Necessary: Avoid enabling Flash unless absolutely necessary. Use alternative solutions whenever possible.
- Enable Flash on Trusted Websites Only: Only enable Flash in Chrome for websites you trust. Avoid visiting suspicious or unknown websites that require Flash.
- Keep Flash Player Updated: If you must use Flash Player, keep it updated to the latest version to patch security vulnerabilities. However, note that Adobe no longer provides updates after December 2020.
- Use a Security Software: Install and maintain a reputable antivirus and firewall software to protect your computer from malware.
- Consider Virtualization: For added security, consider running Flash content in a virtual machine or sandbox environment. This isolates Flash from your main operating system, minimizing the impact of potential security breaches.
Alternatives to Flash
Given the security risks associated with Flash, it’s best to explore alternative solutions whenever possible. Many websites have already migrated to modern web standards like HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript. These technologies offer better performance, security, and cross-browser compatibility.
- HTML5 Video: For video content, HTML5 video is the preferred alternative to Flash. It offers native support in modern browsers and doesn’t require any plugins.
- CSS3 Animations: For animations, CSS3 provides a powerful and efficient way to create visually appealing effects without relying on Flash.
- JavaScript Frameworks: For interactive applications and games, JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js offer robust tools for building complex web experiences.
- WebAssembly: WebAssembly (Wasm) is a binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. Wasm is designed as a portable target for compilation of high-level languages like C/C++/Rust, enabling deployment on the web for client and server applications.
The Future of Web Content
The web is constantly evolving, and technologies like Flash are gradually being replaced by more modern and secure alternatives. Embracing these new technologies is essential for creating web experiences that are both engaging and secure. While you might still need to enable Flash in Chrome in certain situations, it’s important to be aware of the risks and to explore alternative solutions whenever possible.
As the web continues to move away from Flash, developers are focusing on creating content that is accessible, performant, and secure. This shift is beneficial for both users and website owners, as it leads to a better overall web experience. [See also: HTML5 vs Flash: Which is Better?]
Conclusion
While it is possible to enable Flash in Chrome, it’s a practice that should be approached with caution due to the inherent security risks. By understanding the reasons behind Flash’s decline, following the steps outlined in this guide, and exploring alternative solutions, you can minimize the risks and ensure a safer browsing experience. Remember to prioritize security and only enable Flash in Chrome when absolutely necessary on trusted websites.
Ultimately, the future of web content lies in modern technologies like HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript. By embracing these technologies, we can create web experiences that are both engaging and secure, without relying on outdated and vulnerable plugins like Flash. Always consider the security implications before you enable Flash in Chrome.