How Can I Change the Password for My WiFi: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s connected world, a secure WiFi network is paramount. Protecting your home or office network from unauthorized access is crucial for maintaining privacy, preventing bandwidth theft, and safeguarding your connected devices. One of the most effective ways to ensure your network’s security is by regularly changing your WiFi password. This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide on how can I change the password for my WiFi, covering various router types and access methods.
Why You Should Change Your WiFi Password Regularly
Before diving into the ‘how can I change the password for my WiFi‘ process, it’s essential to understand the reasons behind it. Here are several compelling reasons to update your WiFi password periodically:
- Prevent Unauthorized Access: Default or weak passwords are easy targets for hackers. Changing your password reduces the risk of unauthorized users accessing your network.
- Protect Your Data: Unsecured networks can expose your personal data, financial information, and browsing history to malicious actors.
- Maintain Network Performance: Unauthorized users consume bandwidth, slowing down your internet speed. A strong password ensures only authorized devices are connected.
- Comply with Security Best Practices: Regular password updates are a fundamental security practice for any network, whether it’s for personal or business use.
Step-by-Step Guide: How Can I Change the Password for My WiFi
The process of how can I change the password for my WiFi typically involves accessing your router’s settings through a web browser. Here’s a detailed guide:
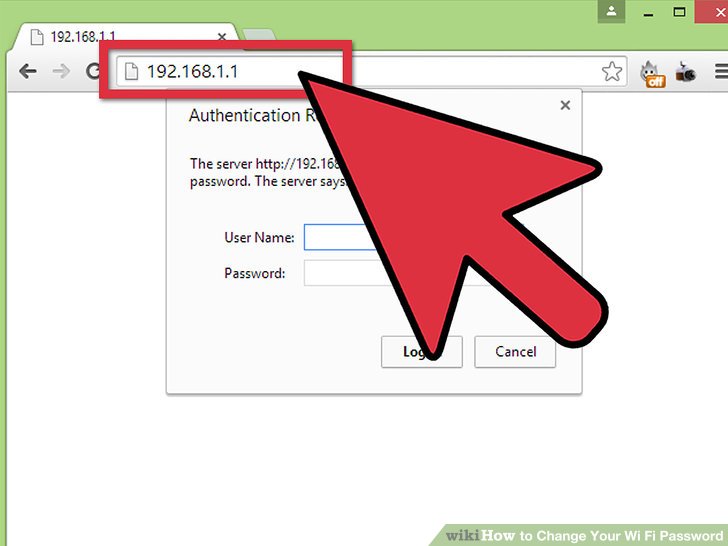
Step 1: Find Your Router’s IP Address
To access your router’s settings, you’ll need its IP address, often referred to as the default gateway. Here’s how to find it on different operating systems:
Windows
- Open the Command Prompt. (Type ‘cmd’ in the search bar and press Enter.)
- Type ‘ipconfig’ and press Enter.
- Look for ‘Default Gateway.’ The address listed is your router’s IP address.
macOS
- Open System Preferences.
- Click on ‘Network.’
- Select your WiFi connection.
- Click ‘Advanced.’
- Go to the ‘TCP/IP’ tab. The router’s IP address is listed next to ‘Router.’
iOS/Android
Finding the router IP on mobile devices is a bit trickier and often requires a third-party app. Many WiFi analyzer apps will display the router’s IP address.
Step 2: Access Your Router’s Settings
Once you have the IP address, follow these steps:
- Open a web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari).
- Type the router’s IP address into the address bar and press Enter.
- You’ll be prompted to enter a username and password. If you haven’t changed them, try the default credentials. Common default usernames are ‘admin’ or ‘user,’ and common default passwords are ‘password’ or ‘admin.’ Consult your router’s manual or the manufacturer’s website if you don’t know the default credentials.
Step 3: Navigate to the Wireless Settings
After logging in, you need to find the wireless settings. The exact location varies depending on the router’s manufacturer and model, but it’s usually found under sections like:
- ‘Wireless’
- ‘WiFi’
- ‘Wireless Settings’
- ‘Security’
Look for a section related to wireless security or password settings.
Step 4: Change Your WiFi Password
Within the wireless settings, you’ll find an option to change your WiFi password. This is usually labeled as ‘Password,’ ‘Passphrase,’ ‘Security Key,’ or ‘WPA/WPA2 Pre-Shared Key.’
- Enter your new password in the designated field.
- Make sure the password is strong and unique. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid using easily guessable information like your name, birthday, or address.
Step 5: Save Your Changes
After entering the new password, click the ‘Save,’ ‘Apply,’ or ‘OK’ button to save the changes. Your router may restart to apply the new settings. This process will temporarily disconnect all devices connected to your WiFi network.
Step 6: Reconnect Your Devices
Once the router has restarted, you’ll need to reconnect all your devices using the new WiFi password. This includes smartphones, tablets, laptops, smart TVs, and any other devices connected to your network.
Tips for Creating a Strong WiFi Password
Creating a strong password is crucial for network security. Here are some tips:
- Use a Long Password: Aim for at least 12 characters. Longer passwords are more difficult to crack.
- Mix Character Types: Include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid Personal Information: Don’t use your name, birthday, address, or other easily guessable information.
- Use a Password Manager: Consider using a password manager to generate and store strong, unique passwords.
- Change Regularly: Update your password every few months to maintain security.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sometimes, changing your WiFi password can present challenges. Here are some common issues and how to resolve them:
- Forgot Router Login Credentials: If you’ve forgotten your router’s username and password, you may need to perform a factory reset. This will erase all custom settings and restore the router to its default configuration. Refer to your router’s manual for instructions on how to perform a factory reset.
- Unable to Access Router Settings: Ensure you’re connected to the router’s network and that you’re using the correct IP address. Try clearing your browser’s cache and cookies or using a different browser.
- Password Not Accepted: Double-check that you’re entering the correct password and that Caps Lock is off. Some routers are case-sensitive.
- Internet Not Working After Password Change: Make sure all devices are reconnected to the WiFi network using the new password. Restart your router and modem if necessary.
Alternative Methods for Changing Your WiFi Password
While accessing the router’s web interface is the most common method, some routers offer alternative ways to change the WiFi password:
- Mobile Apps: Many router manufacturers provide mobile apps that allow you to manage your network settings, including changing the WiFi password. These apps often offer a more user-friendly interface.
- ISP Support: Some internet service providers (ISPs) offer remote support and can assist you in changing your WiFi password. Contact your ISP’s technical support for assistance.
The Importance of WiFi Security
Understanding how can I change the password for my WiFi is just one piece of the puzzle. Maintaining overall WiFi security is crucial to protect your personal information and prevent unauthorized access. Beyond changing your password regularly, consider these additional security measures:
- Enable WPA3 Encryption: WPA3 is the latest and most secure WiFi encryption protocol. If your router supports it, enable WPA3 for enhanced security.
- Disable WPS: WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) is a feature that allows devices to connect to your network easily using a PIN. However, WPS is vulnerable to hacking and should be disabled.
- Enable Guest Network: Create a separate guest network for visitors to use. This prevents them from accessing your main network and sensitive data.
- Keep Router Firmware Updated: Router manufacturers release firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities. Regularly update your router’s firmware to ensure you have the latest security patches.
- Monitor Network Activity: Keep an eye on the devices connected to your network and look for any suspicious activity.
Conclusion
Knowing how can I change the password for my WiFi is a fundamental aspect of maintaining a secure and reliable network. By following the steps outlined in this guide and implementing the recommended security measures, you can protect your network from unauthorized access and ensure your data remains safe. Regular password updates, combined with strong security practices, are essential for safeguarding your digital life in today’s interconnected world. Don’t underestimate the importance of a strong password and proactive security measures – they are your first line of defense against cyber threats.
[See also: Securing Your Home Network: A Comprehensive Guide] [See also: Understanding WiFi Encryption: WPA2 vs WPA3] [See also: Troubleshooting Common WiFi Problems]
