Decoding the Grade: What is the Average Age of a 6th Grader?
Navigating the American education system can feel like deciphering a complex code. One common question parents and educators often ponder is: what is the average age of a 6th grader? While it might seem like a straightforward query, several factors can influence a student’s placement in a particular grade. Understanding these nuances is crucial for ensuring appropriate academic and social-emotional support for every child. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the typical age range for 6th graders, the factors that can affect it, and the implications for students and their families. We’ll delve into the expected age range, discuss common scenarios that deviate from the norm, and offer insights into how schools address these variations.
The Typical Age Range
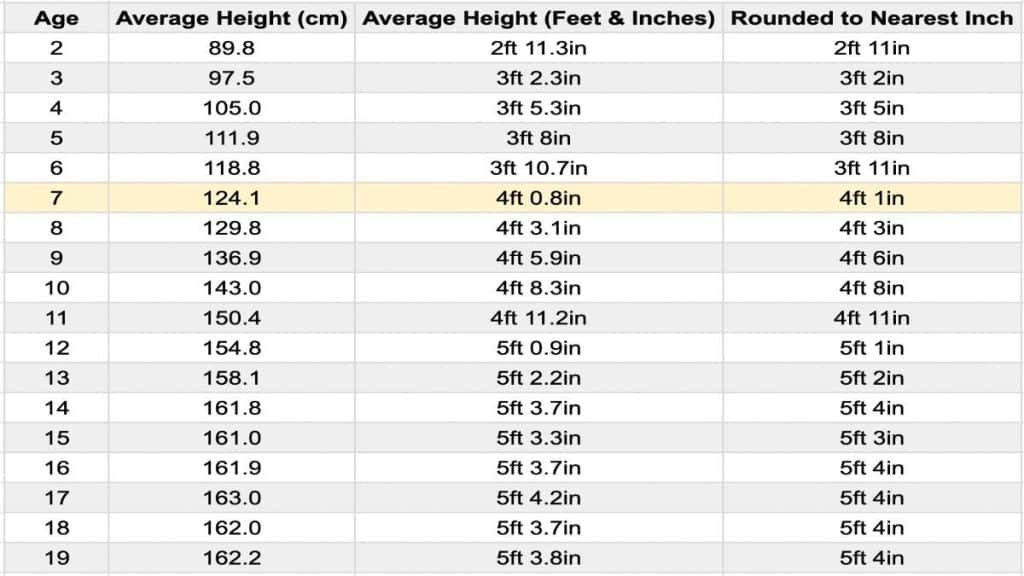
Generally speaking, the average age of a 6th grader falls between 11 and 12 years old. This is based on the assumption that students begin kindergarten around the age of 5 and progress through each grade level without skipping or repeating a year. However, this is just a general guideline, and individual circumstances can significantly alter a student’s grade placement. The average age of a 6th grader is a helpful benchmark but should not be the sole determinant of a student’s academic or social development. The average age of a 6th grader provides a helpful reference point.
Factors Influencing Grade Placement
Several factors can contribute to a student being older or younger than the typical average age of a 6th grader. These include:
- Birthdate: Children born later in the year might start kindergarten a year later, making them slightly older than their classmates throughout their academic journey.
- Early Entrance to Kindergarten: Some states allow children to enter kindergarten early based on assessments and developmental readiness. This can result in students being younger than the average age of a 6th grader by the time they reach middle school.
- Grade Retention (Repeating a Grade): If a student struggles academically or socially in a particular grade, they may be held back to repeat the year. This would naturally make them older than the typical average age of a 6th grader.
- Grade Skipping (Acceleration): In some cases, exceptionally bright or advanced students may be allowed to skip a grade, resulting in them being younger than the average age of a 6th grader.
- Special Education Needs: Students with certain special education needs may be placed in a grade level that aligns with their developmental level rather than their chronological age. This can lead to variations in the average age of a 6th grader within a classroom.
- Transferring from Different School Systems: Educational systems vary across countries and even within different regions of the United States. Transferring from one system to another can sometimes result in a student being placed in a different grade than they would have been in their previous school.
- Homeschooling Background: Students transitioning from homeschooling to traditional schooling may be placed in a grade level based on assessments and evaluations, potentially affecting their alignment with the average age of a 6th grader.
The Impact of Age Differences
While age differences are common in classrooms, it’s important to consider the potential impact on students. A student who is significantly older or younger than their peers may experience social or emotional challenges. Older students might feel out of place or self-conscious about being in a lower grade level, while younger students may struggle to keep up academically or socially with their older classmates.
Educators play a crucial role in addressing these potential challenges. Differentiated instruction, individualized learning plans, and social-emotional support can help ensure that all students, regardless of their age, have the opportunity to thrive. [See also: Strategies for Supporting Students of Varying Ages] Open communication between teachers, parents, and students is essential for identifying and addressing any concerns related to age differences.
Addressing Concerns and Seeking Support
If you have concerns about your child’s grade placement or their social-emotional well-being related to age differences, it’s important to communicate with their teacher and school counselor. They can provide valuable insights and support, and work with you to develop strategies to help your child succeed. Here are some steps you can take:
- Schedule a meeting with your child’s teacher: Discuss your concerns and ask for their observations of your child’s academic and social-emotional progress.
- Consult with the school counselor: The school counselor can provide guidance and support for addressing any social or emotional challenges your child may be facing.
- Consider additional assessments: If you suspect that your child may be misplaced, ask about the possibility of additional assessments to evaluate their academic skills and developmental readiness.
- Advocate for your child’s needs: Work with the school to develop an individualized plan that meets your child’s unique needs and supports their success.
The Role of Schools in Managing Age Variations
Schools have a responsibility to create inclusive and supportive learning environments for all students, regardless of their age. This includes providing differentiated instruction, offering social-emotional support, and addressing any concerns related to age differences. Many schools have policies and procedures in place for addressing grade placement issues and ensuring that students are placed in the most appropriate learning environment.
Furthermore, schools should be proactive in communicating with parents about the factors that influence grade placement and the resources available to support students of all ages. Transparency and open communication are key to building trust and ensuring that all students have the opportunity to succeed.
Beyond the Numbers: Focusing on Individual Development
While understanding the average age of a 6th grader can be helpful, it’s crucial to remember that every child develops at their own pace. Focusing solely on chronological age can be detrimental to a child’s overall well-being. It’s more important to consider their individual academic abilities, social-emotional maturity, and overall developmental readiness when determining the best educational path for them. [See also: Nurturing Individual Learning Styles in Middle School]
Parents and educators should work together to create a supportive and nurturing environment that allows each child to thrive, regardless of their age. This includes celebrating their individual strengths, addressing their challenges, and providing them with the resources and support they need to reach their full potential. The average age of a 6th grader is simply a data point; the real focus should be on the individual student’s journey.
The Average Age of a 6th Grader: A Global Perspective
It’s also worth noting that the average age of a 6th grader can vary significantly across different countries and educational systems. In some countries, children may start school earlier or later than in the United States, which can affect their grade placement at different ages. Additionally, the structure and curriculum of different educational systems can also influence the average age of a 6th grader. For example, some countries may have a longer or shorter primary school cycle, which can impact the age at which students transition to middle school. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the specific context when comparing the average age of a 6th grader across different countries.
The Importance of Social-Emotional Learning
Regardless of a student’s age, social-emotional learning (SEL) plays a vital role in their overall development and success. SEL skills, such as self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making, are essential for navigating the challenges of middle school and beyond. Schools should prioritize SEL programs and initiatives to help students develop these crucial skills. [See also: Integrating Social-Emotional Learning into the Curriculum] Students who have strong SEL skills are better equipped to manage their emotions, build positive relationships, and make responsible choices, regardless of their age or grade level. Addressing the social-emotional needs is just as vital as considering the average age of a 6th grader.
Looking Ahead: Preparing for the Future
As students progress through middle school and beyond, it’s important to continue to support their individual needs and provide them with the resources and opportunities they need to succeed. This includes offering challenging and engaging curriculum, providing access to technology and other resources, and fostering a supportive and inclusive learning environment. By focusing on individual development and providing comprehensive support, we can help all students, regardless of their age, reach their full potential and prepare for a successful future. Understanding the nuances surrounding the average age of a 6th grader is just one piece of the puzzle. The key is to focus on the individual and provide them with what they need to thrive.
In conclusion, while the average age of a 6th grader is generally between 11 and 12 years old, numerous factors can influence a student’s grade placement. It’s crucial to consider individual circumstances, communicate openly with educators, and prioritize the social-emotional well-being of all students. By focusing on individual development and providing comprehensive support, we can ensure that every child has the opportunity to thrive, regardless of their age. Understanding the average age serves as a guide, but the student’s individual journey is paramount. The average age of a 6th grader is a starting point, not a defining characteristic.
