How to Activate Flash in Chrome: A Comprehensive Guide
Adobe Flash Player, once a ubiquitous plugin for web browsers, has largely been phased out due to security concerns and the rise of modern web technologies like HTML5. However, there might still be instances where you need to activate Flash in Chrome to access older websites or specific content. This guide provides a step-by-step approach on how to activate Flash in Chrome, while also highlighting the risks and alternatives.
Understanding the Flash Player Landscape
Before diving into the activation process, it’s crucial to understand why Flash Player is no longer the default choice for web content. Adobe officially ended support for Flash Player on December 31, 2020. Major browsers, including Chrome, have since removed Flash Player entirely or disabled it by default. The primary reasons for this shift include:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Flash Player was prone to numerous security exploits, making it a target for malware and other malicious activities.
- Performance Issues: Flash content often consumed significant system resources, leading to slower browsing experiences and battery drain.
- Modern Alternatives: HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript offer more secure, efficient, and versatile alternatives for creating rich web content.
Despite these drawbacks, some websites still rely on Flash. If you encounter such a site, you might need to temporarily activate Flash in Chrome.
Steps to Activate Flash in Chrome (If Available)
Important Note: Modern versions of Chrome may not support Flash Player at all. These steps are only applicable if your Chrome version still retains some Flash functionality. Proceed with caution and understand the security risks involved.
Step 1: Check Your Chrome Version
First, determine which version of Chrome you are using. Click on the three vertical dots (Menu) in the top-right corner of the Chrome window. Then, navigate to Help > About Google Chrome. Note your Chrome version number.
Step 2: Access Chrome’s Settings
Type chrome://settings/content in the address bar and press Enter. This will take you directly to Chrome’s Content settings.
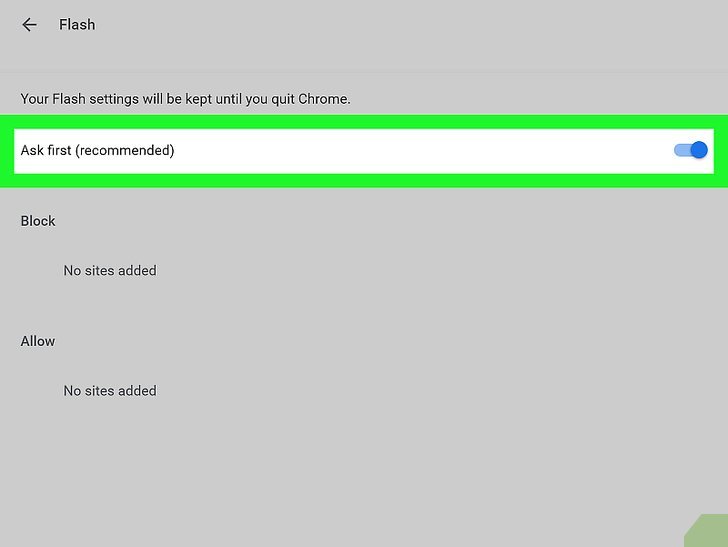
Step 3: Find the Flash Setting
In the Content settings, look for the “Flash” option. If you don’t see it, Flash Player may have been completely removed from your version of Chrome. If you do see it, proceed to the next step.
Step 4: Manage Flash Permissions
Click on the “Flash” option. You will typically see two options:
- Ask first (recommended): This option prompts you to allow Flash each time a website requests it.
- Block sites from running Flash (recommended): This option prevents Flash from running on any website.
To activate Flash in Chrome for specific websites, choose the “Ask first” option. This provides a balance between security and functionality.
Step 5: Allow Flash on Specific Websites
After selecting “Ask first,” you can add specific websites to the “Allow” list. When you visit a website that requires Flash, Chrome will display a prompt asking if you want to allow Flash to run. Click “Allow” to enable Flash for that particular site. The website will then be added to the “Allow” list, so you won’t be prompted again on subsequent visits. Remember that enabling Flash adds a security risk.
Alternative Methods and Considerations
If your version of Chrome does not support Flash, or if you prefer not to enable Flash due to security concerns, consider the following alternatives:
Using an Older Browser Version (Not Recommended)
It is technically possible to use an older version of Chrome that still supports Flash. However, this is strongly discouraged. Older browser versions are vulnerable to security exploits and should not be used for general browsing. Using them opens your computer to potentially serious threats. If you need to activate Flash in Chrome consider other options first.
Using a Flash Emulator or Player
Several Flash emulators and standalone players are available that allow you to run Flash content without a web browser. These emulators often work by converting Flash content into HTML5 or other modern formats. Some popular options include:
- Ruffle: A free and open-source Flash Player emulator written in Rust. Ruffle aims to run old Flash content natively in modern browsers and as a standalone application.
- Lightspark: Another open-source Flash Player implementation.
These emulators may not support all Flash content perfectly, but they can provide a viable alternative to activate Flash in Chrome.
Contacting the Website Owner
If you frequently visit a website that requires Flash, consider contacting the website owner and requesting that they update their content to use modern web technologies like HTML5. This is the most sustainable and secure solution in the long run.
Security Precautions When Activating Flash
If you decide to activate Flash in Chrome, take the following security precautions:
- Only enable Flash on trusted websites: Avoid enabling Flash on unfamiliar or suspicious websites.
- Keep your antivirus software up to date: Ensure that your antivirus software is active and has the latest virus definitions.
- Be cautious of suspicious content: Avoid clicking on links or downloading files from websites that require Flash.
- Disable Flash when not in use: When you’re finished using a website that requires Flash, disable Flash in Chrome to minimize the risk of security vulnerabilities.
[See also: Browser Security Best Practices]
The Future of Flash and Web Content
The decline of Flash Player marks a significant shift in the way web content is created and delivered. Modern web technologies like HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript offer numerous advantages over Flash, including improved security, performance, and accessibility. As more websites migrate to these technologies, the need to activate Flash in Chrome will continue to diminish.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after following these steps, you might encounter issues when trying to activate Flash in Chrome. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Flash Not Working After Activation
If you’ve enabled Flash for a website but it’s still not working, try the following:
- Refresh the page: Sometimes a simple page refresh can resolve the issue.
- Clear your browser cache and cookies: Cached data can sometimes interfere with Flash playback.
- Restart Chrome: Restarting the browser can resolve temporary glitches.
- Check for Chrome updates: Ensure that you are using the latest version of Chrome.
Flash Plugin Crashing
If the Flash plugin crashes frequently, consider the following:
- Update your graphics drivers: Outdated graphics drivers can cause compatibility issues with Flash.
- Disable hardware acceleration: In Chrome’s settings, try disabling hardware acceleration to see if it resolves the crashes.
- Use a different browser: If the crashes persist, try using a different browser to see if the issue is specific to Chrome.
Website Not Detecting Flash
If a website claims that Flash is not installed or enabled, even though you’ve activated Flash in Chrome, try the following:
- Check the website’s requirements: Ensure that the website actually requires Flash and that it is not simply displaying a generic error message.
- Contact the website owner: The website may have a configuration issue that prevents it from detecting Flash correctly.
Conclusion
While the need to activate Flash in Chrome is becoming increasingly rare, this guide provides the necessary steps to do so if you encounter a website that still requires it. However, it’s important to remember the security risks associated with Flash and to consider alternative solutions whenever possible. By understanding the Flash Player landscape and taking appropriate precautions, you can safely access legacy content while minimizing your exposure to potential security threats. Consider using HTML5 alternatives to avoid the need to activate Flash in Chrome. Keep in mind that the best long-term solution is for websites to migrate away from Flash entirely.
