Unlocking Emotions: A Comprehensive Guide to the Emotional Wheel
Understanding and articulating our emotions can be a challenging task. The emotional wheel, a visual tool designed to map and categorize feelings, offers a structured approach to emotional literacy. This guide explores the history, structure, applications, and benefits of using the emotional wheel to enhance self-awareness and improve communication.
What is the Emotional Wheel?
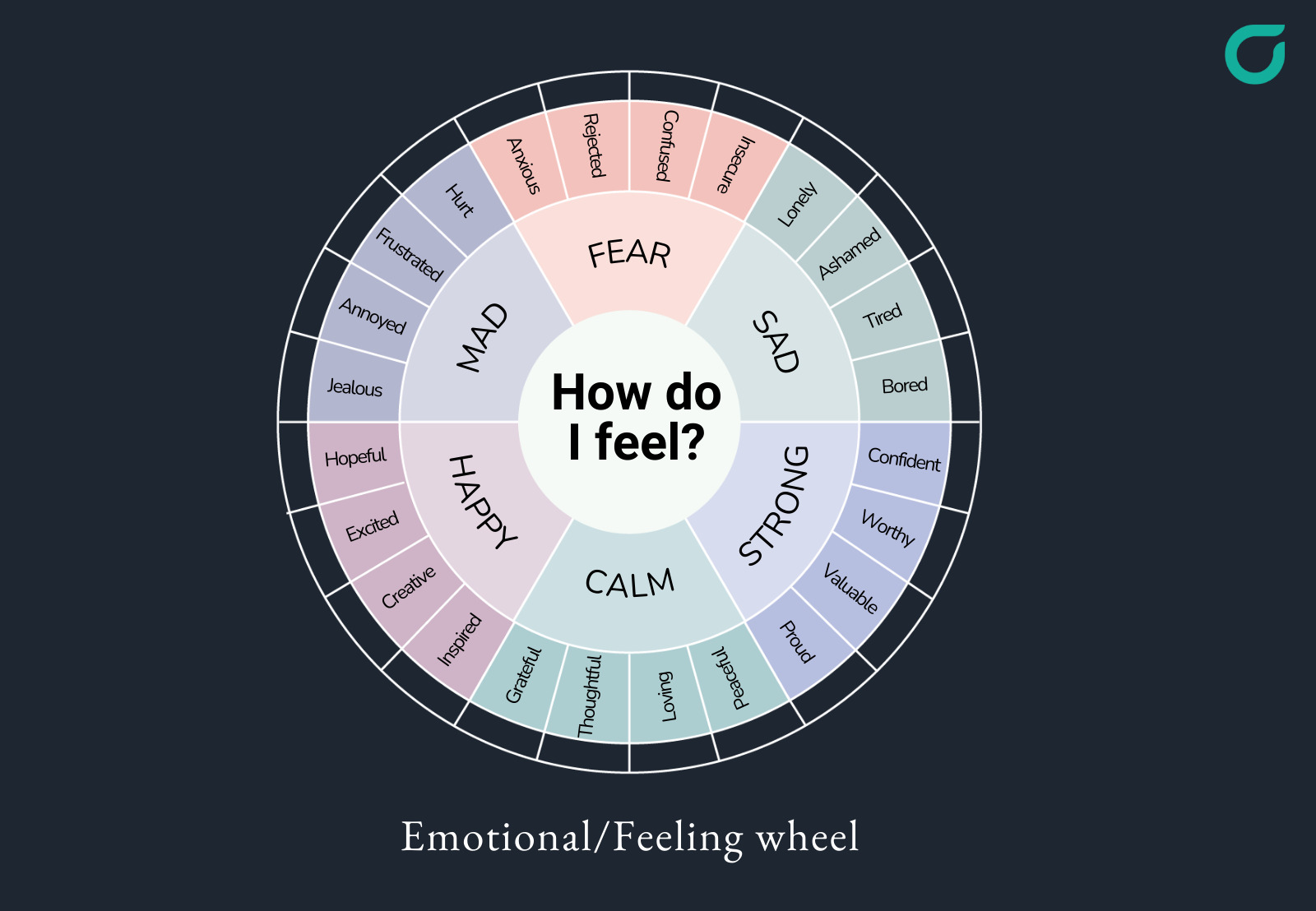
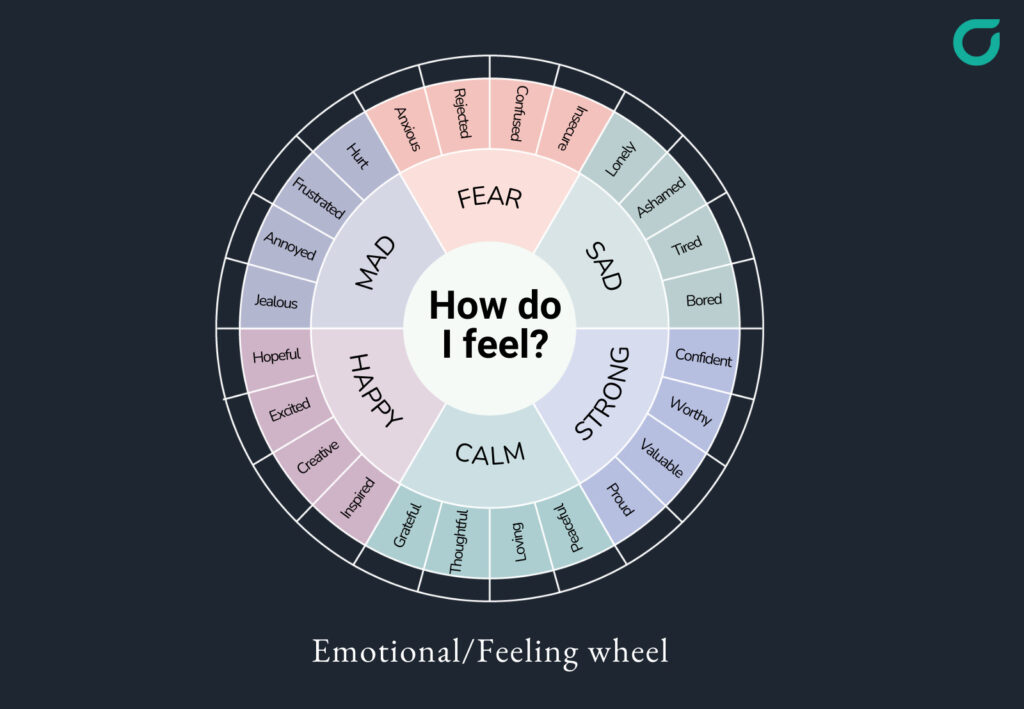
The emotional wheel, also known as the feelings wheel, is a visual representation of human emotions, typically arranged in a circular format. It organizes emotions into categories, starting with core emotions at the center and branching out to more nuanced feelings as you move outward. This design helps individuals identify and label their emotions more precisely. The emotional wheel is a valuable tool for anyone seeking to better understand their internal landscape.
A Brief History
While various iterations of the emotional wheel exist, one of the most recognized versions was developed by Dr. Gloria Willcox in the 1980s. Her work built upon earlier research in psychology and emotions, aiming to create a practical tool for therapists and individuals alike. Later, Robert Plutchik created his own emotional wheel based on his psychoevolutionary theory of emotion, which posits that there are eight basic emotions: joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, disgust, anger, and anticipation. These primary emotions can be combined to form more complex emotions. The emotional wheel continues to evolve, with different versions catering to specific needs and contexts.
Structure of the Emotional Wheel
Most emotional wheels are structured in a hierarchical manner. The center typically features six to eight core emotions, such as joy, sadness, anger, fear, disgust, and surprise. Moving outward, each of these core emotions branches into more specific and nuanced feelings. For example, anger might branch into frustration, irritation, or rage. This layered structure allows users to pinpoint their feelings with greater accuracy.
Core Emotions
The innermost circle of the emotional wheel contains the primary or core emotions. These are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other emotions. Understanding these core emotions is crucial for developing emotional intelligence. Common core emotions include:
- Joy: A feeling of happiness, pleasure, and contentment.
- Sadness: A feeling of sorrow, grief, or disappointment.
- Anger: A feeling of annoyance, frustration, or hostility.
- Fear: A feeling of anxiety, apprehension, or dread.
- Disgust: A feeling of revulsion or aversion.
- Surprise: A feeling of astonishment or amazement.
Secondary and Tertiary Emotions
As you move outward from the core emotions, you encounter secondary and tertiary emotions. These are more complex and specific feelings that arise from combinations or variations of the core emotions. For instance, if you feel joyful, you might also feel content, proud, or optimistic. Understanding these nuances can provide deeper insights into your emotional state. The emotional wheel helps to differentiate between these subtle emotional states.
How to Use the Emotional Wheel
Using the emotional wheel is a straightforward process. Start by identifying the core emotion that most closely aligns with what you’re feeling. Then, move outward along the corresponding branch to explore more specific emotions. Ask yourself questions like: Is it closer to frustration or rage? Is it more like sadness or disappointment? This process of self-inquiry can help you clarify your feelings and understand their intensity.
Steps for Effective Use
- Identify the Core Emotion: Begin by recognizing the primary emotion you’re experiencing.
- Explore the Branches: Move outward along the relevant branch to find more specific feelings.
- Consider the Intensity: Evaluate the intensity of the emotion. Are you mildly annoyed, or are you enraged?
- Reflect on the Cause: Consider what triggered the emotion. Understanding the cause can provide valuable insights.
- Journal Your Thoughts: Write down your feelings and thoughts in a journal to further explore your emotional state.
Benefits of Using the Emotional Wheel
The emotional wheel offers numerous benefits for personal and interpersonal growth. By providing a structured framework for identifying and labeling emotions, it enhances self-awareness, improves communication, and promotes emotional regulation.
Enhanced Self-Awareness
One of the primary benefits of the emotional wheel is its ability to enhance self-awareness. Many people struggle to articulate their feelings beyond simple terms like “happy” or “sad.” The emotional wheel provides a broader vocabulary, allowing individuals to identify and express their emotions with greater precision. This increased self-awareness can lead to a deeper understanding of one’s thoughts, behaviors, and motivations. [See also: Understanding Your Emotions]
Improved Communication
Effective communication relies on the ability to express oneself clearly and accurately. The emotional wheel can improve communication by providing a shared language for discussing emotions. When individuals can articulate their feelings with greater precision, they are better able to communicate their needs and boundaries to others. This can lead to healthier and more fulfilling relationships. The ability to clearly state how you feel, using the emotional wheel as a guide, is a powerful tool.
Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation involves managing and controlling one’s emotional responses. The emotional wheel can assist in this process by helping individuals identify the early signs of emotional distress. By recognizing the subtle shifts in their emotional state, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their emotions before they escalate. For example, if someone notices they are feeling slightly irritated, they can take steps to address the underlying cause before the irritation turns into anger. Regular use of the emotional wheel can improve your emotional regulation skills.
Applications of the Emotional Wheel
The emotional wheel has a wide range of applications across various fields, including therapy, education, and personal development. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for anyone seeking to improve their emotional intelligence.
Therapy and Counseling
Therapists and counselors often use the emotional wheel as a tool to help clients explore their feelings. It can be particularly helpful for individuals who struggle to express their emotions verbally. By pointing to different sections of the wheel, clients can identify and articulate their feelings more easily. The emotional wheel can also facilitate deeper discussions about the underlying causes of emotional distress. [See also: Finding a Therapist]
Education
The emotional wheel can be used in educational settings to teach children and adolescents about emotions. By introducing them to a wide range of feelings, educators can help students develop emotional literacy and empathy. The emotional wheel can also be used to facilitate discussions about conflict resolution and social skills. Teaching children about the emotional wheel from a young age can have a lasting impact on their emotional well-being.
Personal Development
Individuals can use the emotional wheel as a tool for personal development and self-improvement. By regularly checking in with their emotions and using the wheel to identify and label them, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of themselves. This increased self-awareness can lead to more mindful decision-making and healthier relationships. Using the emotional wheel for journaling can be a powerful exercise in self-discovery.
Criticisms and Limitations
While the emotional wheel is a valuable tool, it is not without its criticisms and limitations. Some critics argue that it oversimplifies the complexity of human emotions and that it may not accurately reflect the emotional experiences of all individuals. Additionally, the emotional wheel is a static representation of emotions, while emotions themselves are dynamic and ever-changing.
Cultural Differences
Emotions can be influenced by cultural norms and values. What is considered an acceptable expression of emotion in one culture may be frowned upon in another. The emotional wheel may not fully capture these cultural nuances. It’s important to consider cultural context when using the emotional wheel.
Individual Variation
Each individual experiences emotions in their own unique way. The emotional wheel provides a general framework for understanding emotions, but it may not perfectly align with the emotional experiences of every person. It is important to use the emotional wheel as a guide, rather than a rigid set of rules. Individual emotional experiences should always be validated.
Conclusion
The emotional wheel is a powerful tool for enhancing self-awareness, improving communication, and promoting emotional regulation. By providing a structured framework for identifying and labeling emotions, it empowers individuals to better understand their internal landscape. While it has its limitations, the benefits of using the emotional wheel far outweigh the drawbacks. Whether you are a therapist, educator, or simply someone seeking to improve your emotional intelligence, the emotional wheel can be a valuable resource on your journey. Understanding the emotional wheel and its applications can lead to a more fulfilling and emotionally intelligent life. Embrace the emotional wheel as a guide to navigate the complexities of human emotion and unlock a deeper understanding of yourself and others. The emotional wheel is more than just a diagram; it’s a pathway to emotional clarity and well-being.