How Old is the Average Third Grader? Understanding Grade Level and Age
Understanding the age range of students in different grade levels is a common question for parents, educators, and anyone involved in a child’s education. Specifically, “How old is the average third grader?” is a frequently asked query. This article will delve into the typical age of a third grader, factors that can influence a child’s placement in third grade, and the implications of age differences within the classroom. We will explore the average age, the variations, and other related aspects to give you a comprehensive understanding.
The Typical Age of a Third Grader
The average age of a third grader typically falls between 8 and 9 years old. Children usually start first grade around age 6, second grade at age 7, and third grade at age 8. However, it’s crucial to remember that this is just an average. Several factors can influence when a child enters a specific grade level.
To reiterate, the common answer to “How old is the average third grader?” is 8 or 9. This age range is based on the standard progression through the education system, assuming a child starts school at the typical age. Let’s break down why this is the case.
Standard Progression
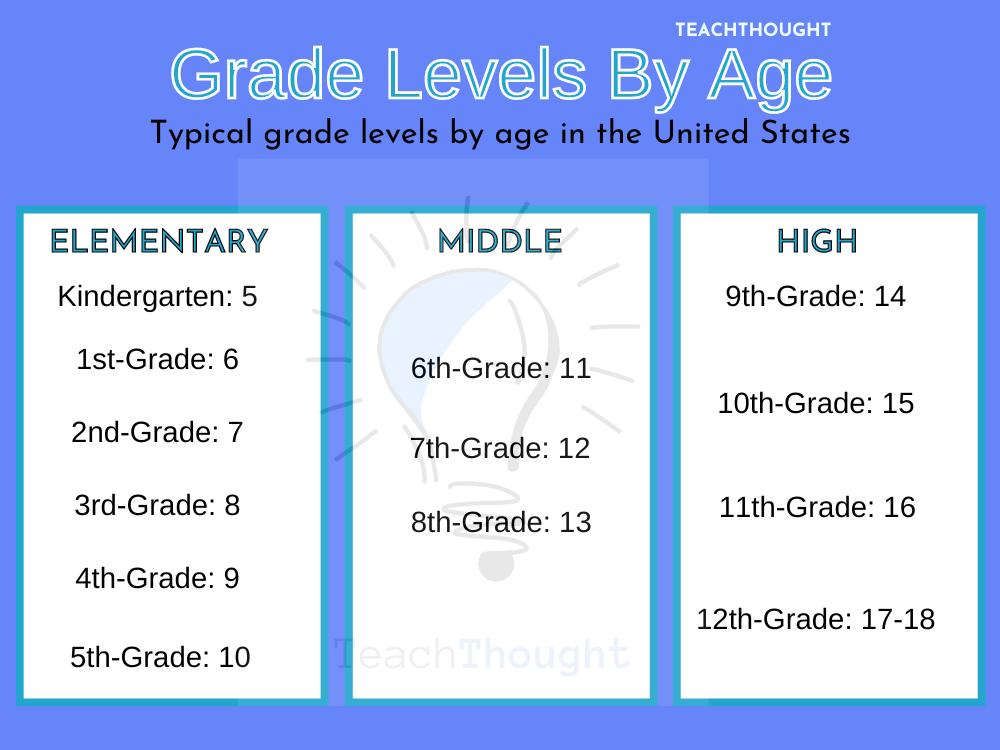
In most school systems, children begin kindergarten around the age of 5. This is the first formal year of schooling. From there, they progress through the grades, typically advancing one grade per year. This standard progression leads to the following age ranges:
- Kindergarten: 5-6 years old
- First Grade: 6-7 years old
- Second Grade: 7-8 years old
- Third Grade: 8-9 years old
- Fourth Grade: 9-10 years old
This linear progression is the foundation for understanding the average age of students in any given grade. So, when considering “How old is the average third grader?”, remember that this is based on the assumption that a child started kindergarten at age 5 and has advanced one grade each year.
Factors Influencing Grade Placement
While the average age provides a general guideline, numerous factors can influence a child’s placement in a particular grade. These factors can result in variations in the age range of students within a third-grade classroom. Understanding these factors is essential for educators and parents.
School Start Dates
One of the primary factors is the school’s cut-off date for enrollment. Many schools have a specific date (e.g., September 1st) that determines whether a child can start kindergarten in a given year. For example, if a child turns five on September 2nd, they might have to wait until the following year to begin kindergarten. This delay can push back their entire academic timeline, making them slightly older than the average student in each subsequent grade.
Therefore, when considering “How old is the average third grader?”, it’s important to know that school start dates significantly influence the age distribution within the classroom.
Early Birthday vs. Late Birthday
Children with birthdays close to the school’s cut-off date can be either among the youngest or the oldest in their class. A child with an early birthday (e.g., January or February) will likely be one of the oldest in their grade, while a child with a late birthday (e.g., August or September) will be one of the youngest. This age difference can impact their academic and social development within the classroom.
The answer to “How old is the average third grader?” becomes more nuanced when considering these birthday variations. A third-grade classroom might include children who are just turning 8 or already approaching 10.
Grade Retention
Grade retention, or repeating a grade, is another factor that can affect a student’s age in a particular grade level. If a student struggles academically or socially, they might be held back to repeat a grade. This means they will be older than their peers in the following year.
When determining “How old is the average third grader?”, keep in mind that some students might be older due to having repeated a grade. This is a common reason for age variations within a classroom.
Grade Skipping
Conversely, some students might be advanced a grade if they demonstrate exceptional academic abilities. This is known as grade skipping or acceleration. A student who skips a grade will be younger than their peers in the higher grade level.
The question “How old is the average third grader?” also has to account for those students who have skipped a grade, making them younger than the typical age range.
International Students
International students who transfer to a new school system might be placed in a grade level that doesn’t align perfectly with their age. This can be due to differences in curriculum, academic standards, or language proficiency. Schools typically assess these students on an individual basis to determine the most appropriate grade placement.
When thinking about “How old is the average third grader?”, remember that the inclusion of international students can introduce further age variations, depending on their previous schooling and placement process.
Implications of Age Differences in the Classroom
Age differences within a classroom can have various implications for students, teachers, and the overall learning environment. Understanding these implications can help educators tailor their teaching strategies and support students effectively.
Academic Performance
Age can be a factor, but not the only factor, in academic performance. Older students might have a slight advantage due to their greater maturity and life experience. However, this isn’t always the case. Younger students can be just as capable and motivated, and individual differences in learning styles and abilities play a more significant role.
The query “How old is the average third grader?” is relevant because age can sometimes correlate with academic readiness, but it’s essential to consider each student’s unique strengths and challenges.
Social and Emotional Development
Social and emotional development can also be influenced by age. Older students might be more socially mature and have better self-regulation skills. They might take on leadership roles within the classroom and serve as role models for younger students.
The answer to “How old is the average third grader?” is important because it helps understand the potential range of social and emotional maturity within the group. Teachers can use this information to foster a supportive and inclusive classroom environment.
Teaching Strategies
Teachers need to be aware of the age range within their classroom and adapt their teaching strategies accordingly. Differentiated instruction, which involves tailoring lessons to meet the individual needs of students, is particularly important when there are significant age differences. This can include providing additional support for younger students or offering more challenging activities for older students.
Knowing “How old is the average third grader?” is just the starting point. Educators must also consider the full spectrum of ages and abilities in their classroom to create effective learning experiences.
Addressing Concerns About Age and Grade Level
Parents sometimes have concerns about whether their child is in the right grade level, especially if their child is significantly older or younger than their peers. It’s essential to address these concerns and work collaboratively with educators to make the best decisions for the child’s well-being and academic success.
Communication with Teachers
Open communication with teachers is crucial. Parents should discuss their concerns with the teacher and seek their input on the child’s progress. Teachers can provide valuable insights into the child’s academic performance, social interactions, and overall development.
When parents ask, “How old is the average third grader?”, they often want to know if their child’s age is affecting their learning experience. Teachers can help address these concerns through regular communication and feedback.
Assessments and Evaluations
Schools can conduct assessments and evaluations to determine whether a student is appropriately placed in their current grade level. These assessments can include standardized tests, classroom observations, and teacher recommendations. The results can help identify any learning gaps or areas where the student might need additional support.
The average age of a third grader is a useful benchmark, but it should not be the sole determinant of grade placement. Assessments provide a more comprehensive understanding of a student’s abilities and needs.
Individualized Education Plans (IEPs)
For students with special needs, an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) can be developed to address their specific learning requirements. An IEP outlines the student’s goals, accommodations, and support services. It can also address concerns related to age and grade level placement.
The question “How old is the average third grader?” is less relevant for students with IEPs, as their education plan is tailored to their unique circumstances and needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the average age of a third grader is typically 8 or 9 years old. However, various factors can influence a child’s placement in third grade, including school start dates, birthdays, grade retention, grade skipping, and international transfers. Age differences within the classroom can have implications for academic performance, social and emotional development, and teaching strategies. Open communication between parents and teachers, along with assessments and evaluations, can help address any concerns related to age and grade level. Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that each child is placed in an environment that supports their individual needs and promotes their overall success.
Understanding “How old is the average third grader?” provides a useful starting point, but it’s essential to remember that every child is unique and deserves personalized attention and support. [See also: Understanding Grade Levels and Academic Expectations] Considering all the factors discussed, educators and parents can work together to create a positive and effective learning experience for all students.
Therefore, while knowing “How old is the average third grader” is helpful, remember it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Focus on individual needs and work with educators to create the best learning environment possible. Remember, understanding “How old is the average third grader” helps set expectations, but it shouldn’t define a child’s potential.
So, the next time someone asks, “How old is the average third grader?”, you can confidently answer, “8 or 9 years old, but it’s more complicated than that!”
