Decoding the Emotions: A Comprehensive Guide to the Feelings Wheel
In the complex tapestry of human experience, emotions play a pivotal role, shaping our thoughts, behaviors, and interactions. However, identifying and articulating these emotions can often be a challenging endeavor. This is where the feelings wheel emerges as a valuable tool. The feelings wheel, a visual representation of emotions, offers a structured and intuitive way to navigate the intricate landscape of human feelings. This article will delve into the history, structure, and practical applications of the feelings wheel, providing a comprehensive guide for anyone seeking to enhance their emotional intelligence.
The Origins and Evolution of the Feelings Wheel
The feelings wheel isn’t a new invention; its roots can be traced back to the field of psychology and emotional literacy. While the exact origins are debated, many attribute the modern iteration to Dr. Gloria Willcox, who developed a version of the feelings wheel in the 1980s. Since then, numerous variations have emerged, each adapting the original concept to suit different needs and contexts. These variations often build upon the core principle of categorizing emotions into concentric circles, moving from broad categories to more specific feelings.
Understanding the Structure of the Feelings Wheel
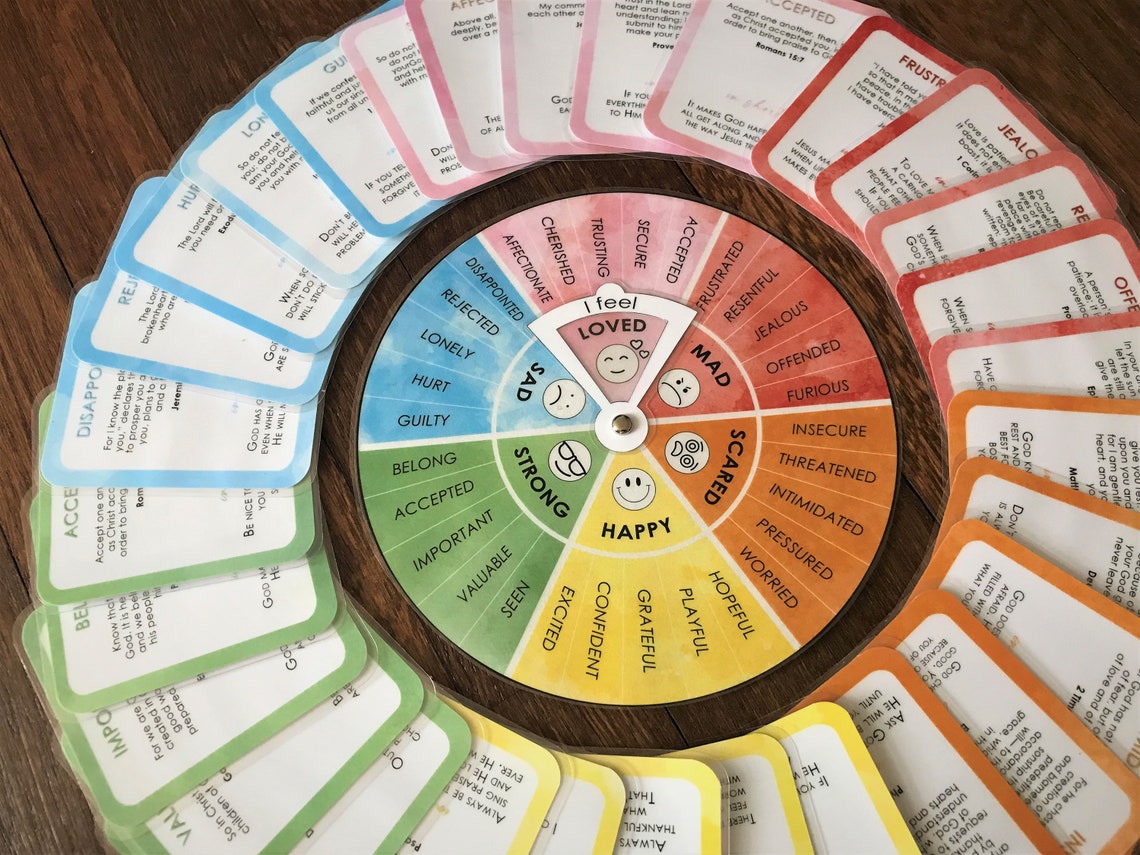
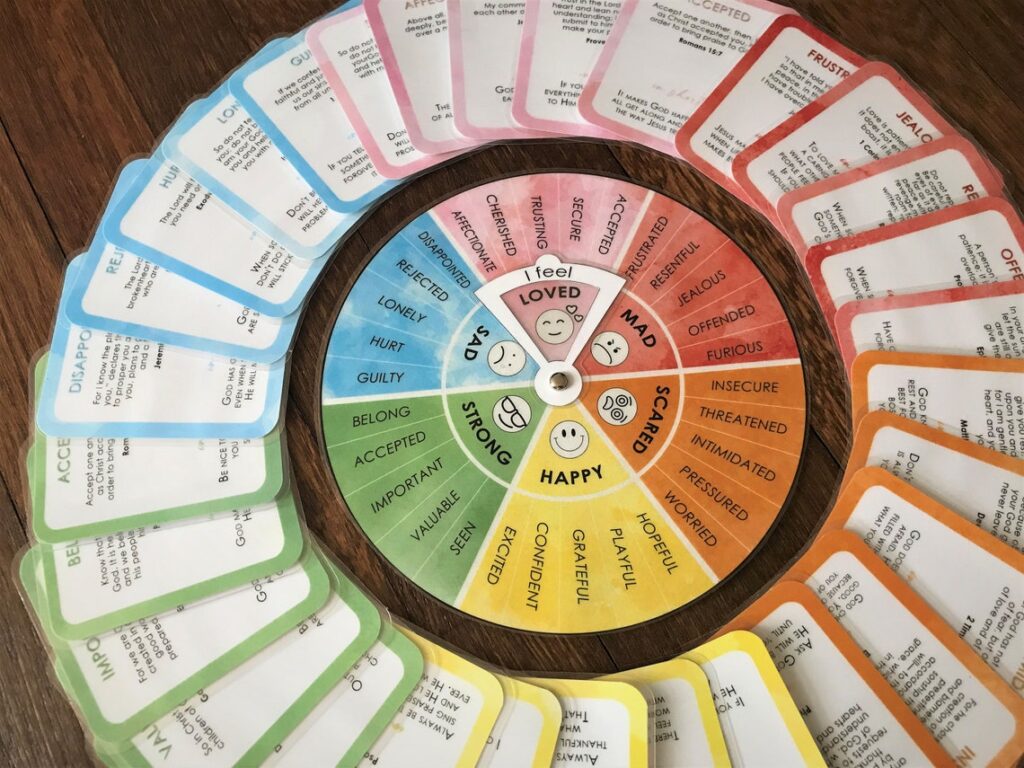
Most feelings wheels share a similar structure, typically consisting of three or more concentric circles. The innermost circle usually contains a few core emotions, such as happiness, sadness, anger, fear, and surprise. The next circle expands upon these core emotions, providing more nuanced variations. For example, under ‘happiness,’ you might find ‘joyful,’ ‘content,’ or ‘optimistic.’ The outermost circle offers even greater specificity, delving into the subtlest shades of feeling. This hierarchical structure allows users to start with a general sense of their emotional state and then gradually narrow down to a more precise description.
Core Emotions
These are the fundamental building blocks of our emotional experience. Recognizing and understanding these core emotions is crucial for developing emotional awareness.
Secondary Emotions
These emotions build upon the core emotions, adding layers of complexity and nuance. They provide a more refined understanding of our emotional state.
Tertiary Emotions
These are the most specific and nuanced emotions, often representing subtle variations of secondary emotions. They allow for a highly detailed and accurate description of our feelings.
How to Use the Feelings Wheel Effectively
The feelings wheel is a versatile tool that can be used in various settings, from personal reflection to therapeutic interventions. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it effectively:
- Identify Your Initial Feeling: Start by acknowledging that you are experiencing an emotion. Don’t judge or suppress it; simply observe it.
- Locate the Core Emotion: Begin with the innermost circle of the feelings wheel and try to identify the core emotion that best aligns with your initial feeling.
- Explore Secondary Emotions: Move to the next circle and explore the secondary emotions that stem from the core emotion you identified. Consider which of these resonate most strongly with your experience.
- Pinpoint Tertiary Emotions: If you need even greater specificity, move to the outermost circle and examine the tertiary emotions. Choose the word that most accurately captures the nuance of your feeling.
- Reflect on Your Emotion: Once you’ve identified your emotion, take some time to reflect on it. Consider what triggered it, how it’s affecting you, and what you can do to manage it effectively.
Benefits of Using a Feelings Wheel
The feelings wheel offers a multitude of benefits for individuals seeking to improve their emotional intelligence and well-being. Some of the key advantages include:
- Enhanced Emotional Awareness: The feelings wheel helps individuals become more attuned to their emotions, enabling them to recognize and understand their feelings more readily.
- Improved Communication: By providing a shared vocabulary for emotions, the feelings wheel facilitates more effective communication and understanding between individuals.
- Greater Self-Understanding: Exploring the feelings wheel can lead to deeper self-understanding, as individuals gain insights into the underlying causes and patterns of their emotions.
- Better Emotional Regulation: Identifying and understanding emotions is the first step towards regulating them effectively. The feelings wheel empowers individuals to manage their emotions in a healthy and constructive manner.
- Reduced Stress and Anxiety: By providing a framework for understanding and processing emotions, the feelings wheel can help reduce stress and anxiety levels.
Applications of the Feelings Wheel in Different Contexts
The feelings wheel is a versatile tool that can be applied in various contexts, including:
Therapy and Counseling
Therapists and counselors often use the feelings wheel to help clients identify and articulate their emotions, particularly those who struggle with emotional expression. It can be a valuable tool for exploring underlying issues and developing coping strategies.
Education
The feelings wheel can be incorporated into educational settings to promote emotional literacy among students. It can help children and adolescents learn to identify and express their emotions in a healthy and constructive way. [See also: Emotional Intelligence in Education]
Personal Development
Individuals can use the feelings wheel as a self-help tool to enhance their emotional awareness and improve their emotional regulation skills. It can be particularly helpful for those who are going through challenging life transitions or experiencing emotional difficulties.
Relationship Building
The feelings wheel can facilitate more effective communication and understanding between partners, family members, and friends. By providing a shared vocabulary for emotions, it can help individuals express their needs and feelings more clearly.
Criticisms and Limitations of the Feelings Wheel
While the feelings wheel is a valuable tool, it’s important to acknowledge its limitations. Some critics argue that the feelings wheel oversimplifies the complexity of human emotions, reducing them to a limited set of categories. Others point out that the feelings wheel is culturally biased, reflecting Western perspectives on emotions. Additionally, the feelings wheel may not be suitable for individuals with certain mental health conditions, such as those who experience alexithymia (difficulty identifying and describing emotions). Despite these limitations, the feelings wheel remains a useful tool for many individuals seeking to enhance their emotional intelligence. [See also: Understanding Alexithymia]
Examples of Different Feelings Wheels
Numerous variations of the feelings wheel exist, each tailored to specific needs and contexts. Some examples include:
- The Core Emotions Wheel: This wheel focuses on the six basic emotions: happiness, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, and disgust.
- The Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions: This wheel, developed by psychologist Robert Plutchik, features eight basic emotions arranged in a circle, with variations in intensity.
- The Positive Psychology Wheel: This wheel emphasizes positive emotions, such as gratitude, joy, and hope.
Practical Exercises Using the Feelings Wheel
To make the most of the feelings wheel, consider incorporating these practical exercises into your daily routine:
- Daily Emotion Check-In: Take a few minutes each day to check in with yourself and identify your emotions using the feelings wheel.
- Journaling: Use the feelings wheel as a prompt for journaling. Write about the emotions you’re experiencing, what triggered them, and how they’re affecting you.
- Mindfulness Meditation: During mindfulness meditation, pay attention to your emotions and use the feelings wheel to label them.
- Role-Playing: Practice using the feelings wheel in role-playing scenarios to improve your communication skills.
The Future of Emotional Literacy and the Feelings Wheel
As emotional intelligence gains increasing recognition as a critical life skill, the feelings wheel is likely to play an even more prominent role in promoting emotional literacy. With ongoing advancements in technology, we can expect to see the development of innovative digital feelings wheels that offer personalized insights and support. Furthermore, the feelings wheel may be integrated into artificial intelligence systems to enhance their ability to understand and respond to human emotions. The journey towards greater emotional awareness and understanding is an ongoing process, and the feelings wheel will undoubtedly continue to be a valuable tool along the way.
Conclusion
The feelings wheel is a powerful tool for decoding the complexities of human emotions. By providing a structured and intuitive framework for identifying and understanding our feelings, it empowers us to enhance our emotional intelligence, improve our communication skills, and cultivate greater self-awareness. Whether used in therapy, education, or personal development, the feelings wheel offers a valuable pathway towards a more emotionally intelligent and fulfilling life. Embracing the feelings wheel is a step towards understanding ourselves and others better, fostering healthier relationships, and navigating the emotional landscape with greater confidence and resilience. The feelings wheel is more than just a diagram; it’s a key to unlocking a deeper understanding of our inner world. [See also: The Importance of Emotional Regulation]