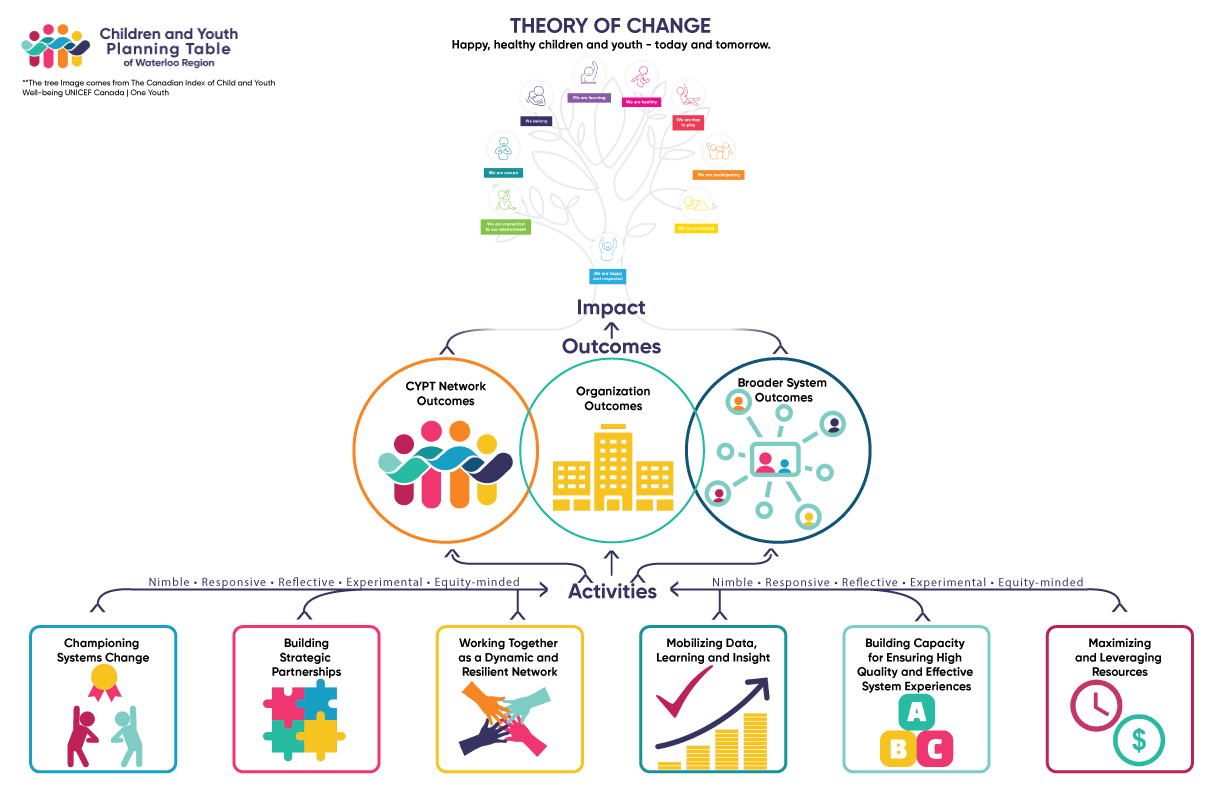
How Children Change: Understanding Developmental Milestones and Influences
Understanding how children change is fundamental to effective parenting, education, and overall societal well-being. Child development is a complex and multifaceted process, influenced by a combination of genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and personal experiences. This article explores the key aspects of child development, highlighting major milestones and the various influences that shape a child’s growth from infancy through adolescence. By examining these changes, we can better support children in reaching their full potential.
The Stages of Child Development
Child development is typically divided into several distinct stages, each characterized by specific physical, cognitive, emotional, and social milestones. These stages provide a framework for understanding the predictable sequence of changes that occur as children mature. However, it’s crucial to remember that every child develops at their own pace, and variations are normal.
Infancy (0-2 years)
Infancy is a period of rapid physical and cognitive growth. During this stage, infants develop fundamental motor skills, such as sitting, crawling, and walking. They also begin to understand object permanence, the concept that objects continue to exist even when they are out of sight. Language development starts with babbling and progresses to the formation of simple words and phrases. Emotional development is centered around forming attachments to caregivers and learning to regulate emotions. This is a critical period for establishing a secure attachment style, which can influence relationships throughout life.
One significant aspect of how children change during infancy is their sensory development. They learn to recognize faces, distinguish between different sounds, and explore their environment through touch, taste, and smell. Early interactions with caregivers play a vital role in stimulating these senses and promoting brain development.
Early Childhood (2-6 years)
Early childhood is a time of significant cognitive and social development. Children in this age group become more independent and begin to engage in imaginative play. They develop a greater understanding of language and can express themselves more clearly. Socially, they learn to interact with peers, share, and take turns. Emotional development involves learning to identify and manage emotions, as well as developing empathy for others. This period is also marked by the development of a sense of self and the beginning of moral reasoning.
Preschool and kindergarten experiences are crucial during this stage, as they provide opportunities for social interaction, cognitive stimulation, and the development of pre-academic skills. Understanding how children change during this period is essential for creating effective early childhood education programs.
Middle Childhood (6-12 years)
Middle childhood is characterized by continued cognitive, social, and emotional development. Children in this age group develop more complex thinking skills, including the ability to reason logically and solve problems. They also become more aware of their own strengths and weaknesses and begin to develop a sense of identity. Socially, they form stronger relationships with peers and become more involved in extracurricular activities. Emotional development involves learning to cope with stress and developing resilience.
Academically, middle childhood is a crucial time for developing foundational skills in reading, writing, and mathematics. Understanding how children change in their cognitive abilities during this period is essential for tailoring educational approaches to meet their needs. [See also: Effective Learning Strategies for Elementary School Students]
Adolescence (12-18 years)
Adolescence is a period of significant physical, cognitive, emotional, and social change. Puberty marks the onset of physical maturity, leading to significant changes in body shape and size. Cognitively, adolescents develop abstract thinking skills and the ability to reason hypothetically. Emotional development is characterized by a search for identity and independence, as well as increased emotional intensity. Socially, adolescents form close relationships with peers and begin to explore romantic relationships.
This stage can be challenging for both adolescents and their parents, as they navigate the complexities of identity formation, peer pressure, and academic expectations. Understanding how children change during adolescence is crucial for providing appropriate support and guidance. [See also: Supporting Teenagers Through Identity Crisis]
Factors Influencing Child Development
Numerous factors influence how children change and develop. These factors can be broadly categorized into genetic, environmental, and experiential influences.
Genetic Influences
A child’s genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining their physical characteristics, temperament, and predisposition to certain conditions. Genes influence brain development, cognitive abilities, and emotional regulation. While genetics provide a foundation, environmental factors can modify gene expression and influence the trajectory of development.
Environmental Influences
The environment in which a child grows up has a profound impact on their development. This includes factors such as family dynamics, socioeconomic status, access to education and healthcare, and cultural norms. A supportive and nurturing environment can promote healthy development, while adverse experiences, such as poverty, neglect, or abuse, can have detrimental effects.
The role of parents and caregivers is particularly important. Responsive and sensitive parenting can foster secure attachment, promote emotional regulation, and support cognitive development. Conversely, inconsistent or harsh parenting can lead to behavioral problems and emotional difficulties. Understanding how children change in response to their environment is crucial for creating supportive and nurturing environments.
Experiential Influences
A child’s experiences, both positive and negative, shape their development. Early experiences, in particular, have a lasting impact on brain development and emotional well-being. Positive experiences, such as engaging in play, learning new skills, and forming meaningful relationships, can promote resilience and foster a sense of competence. Negative experiences, such as trauma or chronic stress, can disrupt development and increase the risk of mental health problems.
The impact of technology and media on child development is also an increasingly important consideration. While technology can offer educational opportunities and facilitate social connection, excessive screen time and exposure to inappropriate content can have negative consequences. Understanding how children change in response to these influences is essential for promoting responsible technology use.
Supporting Healthy Child Development
Supporting healthy child development requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the physical, cognitive, emotional, and social needs of children. This includes providing access to quality healthcare, education, and nutrition, as well as creating safe and nurturing environments. Early intervention programs can be particularly effective in addressing developmental delays and promoting positive outcomes.
Promoting positive parenting practices is also crucial. This includes providing consistent discipline, fostering open communication, and encouraging children to explore their interests and talents. Parents can also model healthy behaviors and provide a supportive and loving environment. Understanding how children change throughout their development can help parents tailor their parenting strategies to meet the evolving needs of their children.
Furthermore, community involvement plays a vital role in supporting child development. Schools, community organizations, and faith-based institutions can provide resources and support for families and children. Creating a strong social support network can help families cope with stress and promote resilience. Understanding how children change within the context of their community is essential for creating effective support systems.
The Importance of Early Childhood Education
Early childhood education (ECE) plays a pivotal role in shaping a child’s future. Quality ECE programs provide children with a structured environment where they can develop essential social, emotional, and cognitive skills. These programs often focus on play-based learning, which encourages creativity, problem-solving, and collaboration. Studies have shown that children who attend high-quality ECE programs are more likely to succeed academically, socially, and emotionally in later life.
ECE also helps to bridge the achievement gap between children from different socioeconomic backgrounds. Children from low-income families often enter school with fewer pre-academic skills than their more affluent peers. ECE programs can help to level the playing field by providing these children with the necessary skills and support to succeed. Understanding how children change through early education is crucial for promoting equity and opportunity.
Addressing Developmental Delays
Developmental delays occur when a child does not reach developmental milestones within the expected timeframe. These delays can affect various areas of development, including motor skills, language, cognitive abilities, and social-emotional development. Early identification and intervention are crucial for addressing developmental delays and maximizing a child’s potential.
Parents and caregivers should be aware of the typical developmental milestones for each age group and consult with a healthcare professional if they have concerns about their child’s development. Early intervention services can provide specialized support and therapy to help children overcome developmental delays. Understanding how children change with intervention is vital for improving outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding how children change is essential for creating a society that supports the healthy development of all children. By recognizing the stages of development, the factors that influence growth, and the importance of early intervention, we can empower children to reach their full potential. Continued research and advocacy are needed to ensure that all children have access to the resources and support they need to thrive. [See also: The Future of Child Development Research]
The journey of childhood is a remarkable and transformative one. By understanding the complexities of child development, we can better support children in navigating the challenges and opportunities they face, ultimately contributing to a brighter future for all.