How to Activate Flash Player on Chrome: A Comprehensive Guide
Adobe Flash Player, once a ubiquitous plugin for web browsers, powered a vast array of online content, from interactive games and animations to video playback. While its use has significantly declined due to security vulnerabilities and the rise of HTML5, there are still instances where you might need to activate Flash Player on Chrome. This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide on how to enable Flash Player in Chrome, along with important considerations and alternatives.
Understanding Flash’s Decline
Before diving into the activation process, it’s crucial to understand why Flash Player has become less prevalent. Adobe officially ended support for Flash Player on December 31, 2020. Major browsers, including Chrome, have since removed Flash Player entirely or require explicit user permission to run it. This decision was driven by several factors:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Flash Player was notorious for security flaws that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Performance Issues: Flash content often consumed significant system resources, leading to slow performance and battery drain.
- HTML5 Alternatives: Modern web technologies, particularly HTML5, offer superior performance, security, and cross-platform compatibility.
Despite its decline, some legacy websites or applications still rely on Flash. If you encounter such content, here’s how to activate Flash Player on Chrome.
Steps to Activate Flash Player on Chrome
While Google Chrome has officially phased out Flash Player, there are still methods to enable it, though they are generally discouraged due to security risks. These steps are provided for informational purposes only, and you should proceed with caution.
Method 1: Using the Chrome Settings (If Flash is Still Present)
This method applies if your Chrome version still has remnants of Flash Player functionality. Note that this is increasingly rare.
- Open Chrome Settings: Click the three vertical dots (Menu) in the top-right corner of Chrome and select “Settings.”
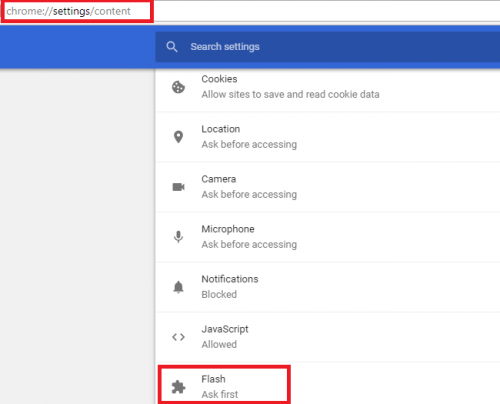
- Navigate to Site Settings: In the Settings menu, type “Flash” in the search bar or navigate to “Privacy and security” and then “Site settings.”
- Find Flash Settings: Look for “Flash” or “Adobe Flash” in the list of site settings.
- Enable Flash: If you see the Flash setting, toggle the switch to “Ask first” or “Allow sites to run Flash.” The exact wording may vary depending on your Chrome version.
- Manage Exceptions: You can add specific websites to the “Allow” list to enable Flash only on trusted sites. Click “Add” and enter the URL of the website.
Method 2: Using the Chrome Component Updater (Potentially Outdated)
In older versions, you might have been able to re-enable Flash through Chrome’s component updater. This method is likely ineffective now.
- Type in Chrome Address Bar: Type `chrome://components` into the Chrome address bar and press Enter.
- Find Adobe Flash Player: Locate “Adobe Flash Player” in the list of components.
- Check for Updates: Click the “Check for updates” button. If an update is available, Chrome will download and install it.
- Restart Chrome: After the update, restart Chrome and check if Flash is enabled.
Method 3: Using a Browser Extension (Use with Extreme Caution)
Some browser extensions claim to enable Flash Player functionality. However, these extensions often come with significant security risks and may contain malware. Use them only as a last resort and from trusted sources.
- Search for Flash Player Extensions: Go to the Chrome Web Store and search for “Flash Player.”
- Evaluate Extensions Carefully: Before installing any extension, check its reviews, permissions, and developer information. Be wary of extensions with low ratings, excessive permissions, or unknown developers.
- Install and Configure: If you choose to install an extension, follow the instructions provided by the extension developer.
Warning: Using third-party extensions to activate Flash Player on Chrome comes with inherent risks. Ensure the extension is from a reputable source and monitor your system for any unusual behavior after installation.
Risks of Enabling Flash Player
Enabling Flash Player, even temporarily, can expose your computer to security risks. Flash Player has a history of security vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious websites. These vulnerabilities can allow attackers to:
- Install Malware: Inject malicious code onto your computer without your knowledge.
- Steal Data: Access sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, and personal data.
- Control Your Computer: Take control of your computer remotely.
Therefore, it is strongly recommended to avoid enabling Flash Player unless absolutely necessary. If you must enable it, do so only for trusted websites and disable it immediately afterward.
Alternatives to Flash Player
Given the risks associated with Flash Player, it’s best to explore alternatives whenever possible. Modern web technologies like HTML5, JavaScript, and CSS3 offer robust solutions for creating interactive web content.
- HTML5 Video: Use HTML5 video elements to play videos without requiring Flash Player.
- JavaScript Libraries: Utilize JavaScript libraries like Three.js and Phaser to create interactive games and animations.
- WebAssembly: WebAssembly provides a high-performance alternative for complex applications that previously relied on Flash Player.
Many websites and applications have already migrated from Flash to these modern technologies. If you encounter a website that still requires Flash, consider contacting the website owner and suggesting they update their content.
Troubleshooting Flash Player Activation
If you encounter issues while trying to activate Flash Player on Chrome, here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Check Chrome Version: Ensure you are using the latest version of Chrome. Outdated versions may have different settings or compatibility issues.
- Clear Cache and Cookies: Clearing your browser’s cache and cookies can resolve conflicts that may prevent Flash from working correctly.
- Disable Conflicting Extensions: Some browser extensions may interfere with Flash Player. Try disabling other extensions to see if that resolves the issue.
- Reinstall Chrome: If all else fails, try reinstalling Chrome. This can fix corrupted files or settings that may be causing problems.
- Consult Chrome Help: Refer to the official Chrome help documentation for more troubleshooting steps.
Conclusion
While the need to activate Flash Player on Chrome is becoming increasingly rare, there may be situations where it’s necessary to access legacy content. However, enabling Flash Player carries significant security risks, and it’s essential to proceed with caution. Whenever possible, explore alternatives like HTML5 and JavaScript to avoid using Flash altogether. Always ensure you are using the latest version of Chrome and keep your system secure by disabling Flash Player when not in use. Remember to only activate Flash Player on Chrome for websites you trust implicitly.
By understanding the risks and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions about whether to activate Flash Player on Chrome and minimize the potential security impact.
Ultimately, the best approach is to encourage websites that still rely on Flash to migrate to modern web technologies. This will ensure a safer and more efficient browsing experience for everyone.
[See also: Chrome Browser Security Best Practices]
[See also: Troubleshooting Common Chrome Errors]
