How to Block Website Redirects: A Comprehensive Guide
Website redirects are a common part of the internet experience. They can be used for legitimate purposes, such as moving a website to a new domain or directing users to a specific page. However, they can also be used for malicious purposes, such as phishing scams or malware distribution. Knowing how to block website redirects is crucial for maintaining online security and ensuring a smooth browsing experience.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various methods you can use to block website redirects, discuss the reasons why you might want to do so, and provide practical tips to enhance your overall online safety. We’ll cover everything from browser settings and extensions to more advanced techniques.
Understanding Website Redirects
Before diving into how to block website redirects, it’s important to understand what they are and how they work. A website redirect is a process that automatically sends a user from one URL to another. This can happen for several reasons:
- Moving a website: When a website changes its domain name, redirects are used to send users from the old domain to the new one.
- URL shortening: Services like bit.ly use redirects to shorten long URLs, making them easier to share.
- A/B testing: Redirects can be used to direct different users to different versions of a webpage to test which version performs better.
- Affiliate marketing: Affiliate links often use redirects to track sales and commissions.
While many redirects are legitimate, some are used for malicious purposes. These are the ones we want to block website redirects from performing.
Why Block Website Redirects?
There are several compelling reasons to block website redirects, primarily related to security and user experience:
- Preventing Phishing Scams: Phishing websites often use redirects to disguise their true URL. By blocking website redirects, you can make it harder for these scams to succeed.
- Avoiding Malware Distribution: Some malicious websites use redirects to send users to sites that automatically download malware.
- Enhancing Privacy: Redirects can be used to track your online activity. By blocking website redirects, you can limit the amount of data that websites can collect about you.
- Improving Browsing Speed: Excessive redirects can slow down your browsing experience. Blocking website redirects can help speed things up.
- Reducing Annoyance: Some redirects are simply annoying, such as those used to display unwanted advertisements.
Methods to Block Website Redirects
Now, let’s explore the various methods you can use to block website redirects.
Browser Settings
Most modern web browsers offer some built-in features that can help you block website redirects. While these features may not completely eliminate redirects, they can provide a basic level of protection. Here’s how to configure these settings in popular browsers:
Google Chrome
Chrome doesn’t have a direct setting to block website redirects. However, you can enhance security by enabling the “Safe Browsing” feature:
- Click on the three dots in the top-right corner of the Chrome window.
- Select “Settings.”
- Click on “Privacy and security.”
- Click on “Security.”
- Choose “Enhanced protection” or “Standard protection” for Safe Browsing.
These options will warn you about potentially dangerous websites, including those that use malicious redirects. Also, keep Chrome updated, as updates often include security improvements that implicitly help block website redirects that lead to harmful sites.
Mozilla Firefox
Firefox also doesn’t have a direct setting to block website redirects, but it offers strong privacy and security features that can help mitigate the risks associated with them:
- Click on the three horizontal lines in the top-right corner of the Firefox window.
- Select “Settings.”
- Click on “Privacy & Security.”
- Under “Enhanced Tracking Protection,” choose “Standard,” “Strict,” or “Custom.” The “Strict” setting offers the highest level of protection.
Firefox also has a feature called “DNS over HTTPS (DoH),” which encrypts your DNS queries and makes it harder for attackers to intercept and redirect your traffic. Enabling DoH can indirectly help block website redirects used for malicious purposes.
Safari
Safari is known for its strong privacy features, which can help block website redirects used for tracking. To enhance security:
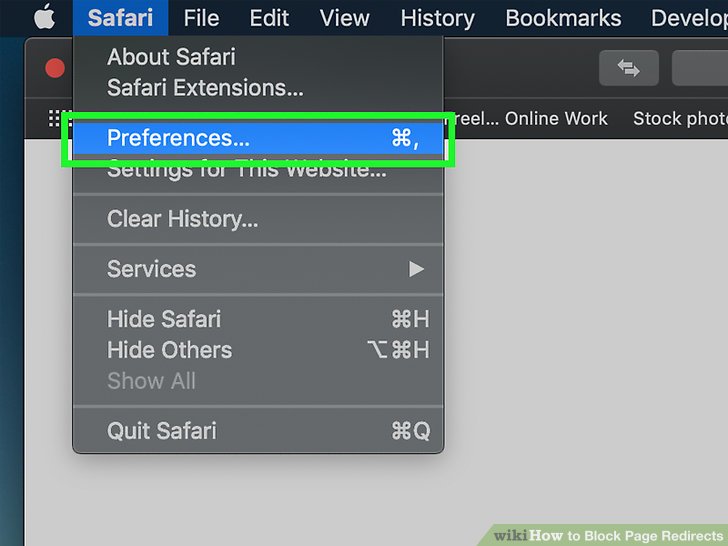
- Open Safari and go to “Safari” in the menu bar.
- Select “Preferences.”
- Click on “Privacy.”
- Check the box next to “Prevent cross-site tracking.”
This setting will help prevent websites from tracking you across different domains, which can reduce the number of redirects you encounter.
Browser Extensions
Browser extensions are a more effective way to block website redirects. There are many extensions available that can automatically detect and block malicious redirects. Here are a few popular options:
- Redirect Remover: This extension automatically removes redirects from URLs, taking you directly to the final destination.
- uBlock Origin: While primarily an ad blocker, uBlock Origin can also block website redirects used for advertising and tracking.
- Privacy Badger: This extension automatically learns to block website redirects that track you without your consent.
- HTTPS Everywhere: While not directly related to redirect blocking, HTTPS Everywhere ensures that you are always using a secure connection, which can help prevent man-in-the-middle attacks that involve redirects.
To install a browser extension, simply visit the Chrome Web Store, Firefox Add-ons, or Safari Extensions Gallery and search for the extension you want to install. Once installed, the extension will automatically block website redirects according to its settings.
Using a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in a different location. This can help block website redirects by making it harder for websites to track your location and redirect you based on your geographical location. Additionally, some VPNs offer built-in malware and phishing protection, which can further enhance your security.
When choosing a VPN, make sure to select a reputable provider with a strong privacy policy. Some popular VPN providers include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, and Surfshark.
Adjusting DNS Settings
Your Domain Name System (DNS) settings determine how your computer translates domain names (like example.com) into IP addresses. By using a secure DNS provider, you can help block website redirects used for malicious purposes. Some popular secure DNS providers include Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) and Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
To change your DNS settings, follow these steps:
Windows
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click on “Network and Internet.”
- Click on “Network and Sharing Center.”
- Click on “Change adapter settings.”
- Right-click on your network adapter and select “Properties.”
- Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click on “Properties.”
- Select “Use the following DNS server addresses.”
- Enter the DNS server addresses for your chosen provider.
- Click “OK” to save your changes.
macOS
- Open System Preferences.
- Click on “Network.”
- Select your network connection and click on “Advanced.”
- Click on the “DNS” tab.
- Click on the “+” button to add new DNS server addresses.
- Enter the DNS server addresses for your chosen provider.
- Click “OK” to save your changes.
Using a Firewall
A firewall is a security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. By configuring your firewall to block website redirects from known malicious domains, you can add an extra layer of protection. Most operating systems have a built-in firewall, and there are also many third-party firewall applications available.
To configure your firewall, you will need to add rules that block website redirects from specific domains or IP addresses. This can be a complex process, but there are many online resources that can help you get started.
Tips for Staying Safe Online
In addition to blocking website redirects, there are several other steps you can take to stay safe online:
- Keep your software up to date: Software updates often include security patches that can protect you from the latest threats.
- Use strong passwords: Use a different, strong password for each of your online accounts. A password manager can help you keep track of your passwords.
- Be careful what you click on: Avoid clicking on links in emails or on websites that you don’t trust.
- Install an antivirus program: An antivirus program can help protect you from malware and other threats.
- Be wary of suspicious websites: If a website looks suspicious, don’t enter any personal information or download any files.
Conclusion
Blocking website redirects is an important step in protecting yourself from online threats. By using the methods outlined in this guide, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to phishing scams, malware distribution, and other malicious activities. Remember to combine these techniques with other security best practices to create a comprehensive defense against online threats. Staying informed and proactive is key to maintaining a safe and enjoyable online experience.
By understanding the risks associated with redirects and implementing the appropriate safeguards, you can browse the internet with greater confidence and peace of mind. Regularly review your security settings and stay updated on the latest threats to ensure that you are always protected. [See also: How to Identify Phishing Websites] [See also: Best VPNs for Online Security]
