How to Enable Flash on Chrome: A Comprehensive Guide
Adobe Flash, once a cornerstone of web browsing, has reached its end-of-life. Major browsers, including Google Chrome, have officially discontinued support for Flash Player. However, there might be instances where you still need to enable Flash on Chrome, particularly for accessing legacy content or specific intranet applications. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed, fact-checked, and secure approach to understanding and, if absolutely necessary, enabling Flash on Chrome.
Understanding the Risks of Enabling Flash
Before delving into the ‘how-to,’ it’s crucial to understand why Flash has been deprecated. Adobe Flash Player is riddled with security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors to inject malware, steal data, or compromise your system. Modern web technologies like HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript offer more secure and efficient alternatives, rendering Flash obsolete. Enabling Flash on Chrome significantly increases your risk of exposure to security threats. Therefore, consider this option only as a last resort, and only for trusted websites.
Why You Might Need to Enable Flash (Temporarily)
Despite the risks, a few legitimate scenarios might necessitate enabling Flash:
- Accessing Legacy Websites: Some older websites haven’t been updated to modern standards and still rely on Flash for content rendering.
- Intranet Applications: Certain internal applications within organizations might still utilize Flash.
- Specific Games or Educational Content: A small number of online games or educational resources may still require Flash.
If you find yourself in one of these situations, proceed with extreme caution and only enable Flash for the specific website that requires it. Avoid enabling Flash globally.
Steps to Enable Flash on Chrome (If Absolutely Necessary)
Important Note: These steps are provided for informational purposes only. We strongly advise against enabling Flash unless absolutely necessary. Ensure your antivirus software is up-to-date before proceeding.
Checking Your Chrome Version
First, ensure your Google Chrome browser is up-to-date. While Chrome no longer supports Flash by default, older versions might still have remnants of the Flash plugin. Updating to the latest version minimizes potential vulnerabilities. To check your Chrome version:
- Click on the three vertical dots (Menu) in the top-right corner of Chrome.
- Go to Help > About Google Chrome.
- Chrome will automatically check for updates and install them if available.
Enabling Flash on a Specific Website (Using the Site Settings)
This is the recommended method for enabling Flash, as it limits the risk to a single, trusted website. This method might not work on the latest versions of Chrome, as Flash support is increasingly being removed.
- Visit the Website: Navigate to the website that requires Flash.
- View Site Information: Click on the padlock icon (or the ‘Not Secure’ warning) in the address bar, to the left of the website’s URL.
- Site Settings: Select ‘Site Settings’.
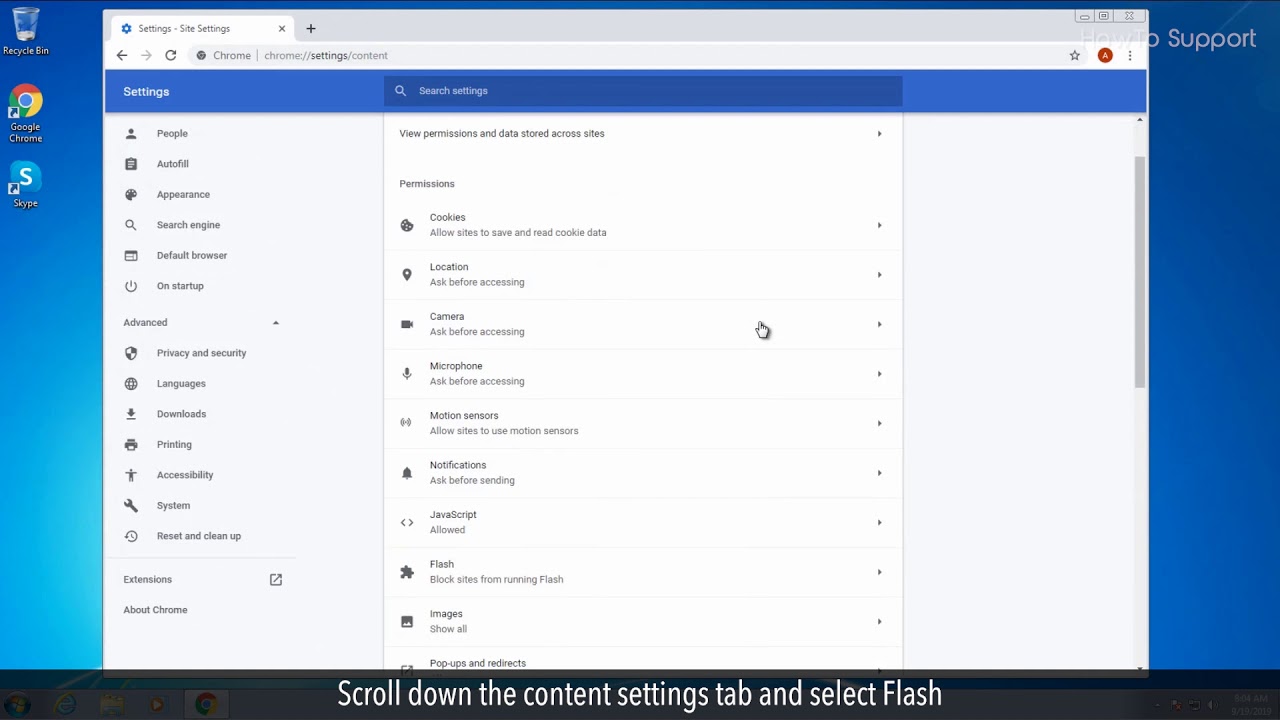
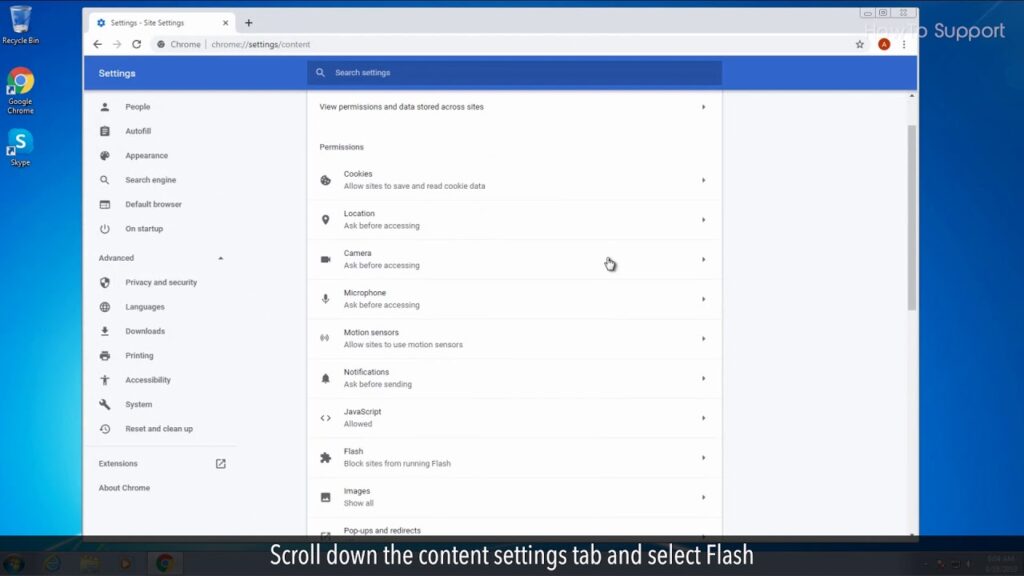
- Find Flash: Scroll down to find the ‘Flash’ setting.
- Allow Flash: In the dropdown menu next to ‘Flash’, select ‘Allow’.
- Reload the Page: Refresh the page. Chrome may prompt you to reload the page to activate Flash.
Enabling Flash Globally (Not Recommended)
Warning: Enabling Flash globally is highly discouraged due to the significant security risks involved. Only proceed with this method if absolutely necessary and if you understand the potential consequences. This method may not work on the latest versions of Chrome.
- Type in Chrome Flags: In the Chrome address bar, type
chrome://flagsand press Enter. - Search for Flash: Use the search box at the top of the page to search for ‘Flash’.
- Enable ‘Run all Flash content’: Find the ‘Run all Flash content’ flag and set it to ‘Enabled’.
- Relaunch Chrome: Click the ‘Relaunch’ button at the bottom of the page to restart Chrome.
Even after enabling this flag, you may still need to grant permission for Flash on individual websites using the Site Settings method described above. This is because Chrome is progressively removing Flash support.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after enabling Flash using the methods above, you might encounter issues. Here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Ensure Flash is Installed: Although Chrome includes a built-in Flash plugin, ensure that Adobe Flash Player is installed on your system. You can download it from Adobe’s website (though Adobe no longer supports or recommends its use).
- Check Flash is Enabled in Chrome Settings: Double-check that Flash is enabled in Chrome’s Site Settings for the specific website.
- Clear Chrome’s Cache and Cookies: Cached data or cookies can sometimes interfere with Flash. Clear your browser’s cache and cookies and try again.
- Update Chrome: Ensure you’re using the latest version of Chrome.
- Disable Extensions: Some browser extensions can conflict with Flash. Try disabling your extensions one by one to see if any are causing the issue.
- Reinstall Chrome: As a last resort, try reinstalling Chrome.
Alternatives to Enabling Flash
Before resorting to enabling Flash, consider these alternatives:
- Contact the Website Owner: Request that the website owner update their content to modern standards like HTML5.
- Search for Alternative Content: Look for alternative versions of the content that don’t require Flash.
- Use a Virtual Machine: If you absolutely need to access Flash content, consider using a virtual machine with an older browser version that still supports Flash. This isolates the risk to the virtual machine and protects your main system.
The Future of Flash
Adobe has officially ended support for Flash Player. Browsers are actively removing Flash support. It’s crucial to understand that enabling Flash is a temporary solution at best. The long-term solution is to migrate to modern web technologies. Website owners should prioritize updating their content, and users should seek alternatives to Flash-based content. The end of Flash is a positive step towards a more secure and efficient web.
Conclusion: Enabling Flash on Chrome with Caution
While this guide provides instructions on how to enable Flash on Chrome, it’s vital to reiterate the security risks involved. Only enable Flash if absolutely necessary, and only for trusted websites. Keep your browser and antivirus software up-to-date, and consider the alternatives mentioned above. The web is evolving, and embracing modern technologies is the best way to ensure a secure and enjoyable browsing experience. Remember to disable Flash immediately after using the Flash-dependent content. The risks associated with enabling Flash on Chrome are significant, and should not be taken lightly. Always prioritize your online safety.
If you are looking for more information on browser security, [See also: Best Practices for Browser Security]. For tips on improving your overall online safety, [See also: Comprehensive Guide to Online Security]. And for insights into the future of web technologies, [See also: The Evolution of Web Development].