Mastering SSIS Data Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a powerful platform for building high-performance data integration and workflow solutions. SSIS data capabilities are essential for organizations looking to consolidate data from various sources, cleanse and transform it, and load it into data warehouses or other target systems. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core concepts of SSIS, its architecture, key components, and best practices for designing and deploying robust data integration solutions. We’ll explore how SSIS data transformations can streamline ETL processes, improve data quality, and ultimately drive better business intelligence.
Understanding SSIS Architecture
At its heart, SSIS is an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool. Its architecture is designed to handle complex data workflows efficiently. The core components of SSIS include:
- Control Flow: Defines the sequence of tasks to be executed. It’s the backbone of your SSIS package, controlling the order in which data is extracted, transformed, and loaded.
- Data Flow: Handles the actual movement and transformation of data. This is where you define your data sources, transformations, and destinations.
- Connections Managers: Provide connectivity to various data sources such as databases, files, and web services.
- Tasks: Represent individual units of work, such as executing SQL statements, transferring files, or sending emails.
- Data Flow Components: These are the building blocks of the data flow, including sources, transformations, and destinations.
The SSIS runtime engine executes the packages, managing the flow of data and control based on the defined workflows. Understanding this architecture is crucial for designing efficient and scalable SSIS solutions.
Key SSIS Data Integration Components
SSIS offers a rich set of data integration components that enable you to perform a wide range of ETL operations. Some of the most important components include:
- Sources: Extract data from various sources, such as SQL Server, Oracle, Excel files, and flat files.
- Transformations: Cleanse, transform, and enrich data. Common transformations include data conversion, aggregation, sorting, and lookup.
- Destinations: Load data into target systems, such as SQL Server, Oracle, and flat files.
Common SSIS Transformations
SSIS provides a wide array of transformations to manipulate data. Here are a few commonly used ones:
- Data Conversion Transformation: Converts data from one data type to another.
- Derived Column Transformation: Creates new columns based on existing columns and expressions.
- Aggregate Transformation: Performs aggregations such as SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX.
- Lookup Transformation: Retrieves data from a lookup table based on matching values in the input data.
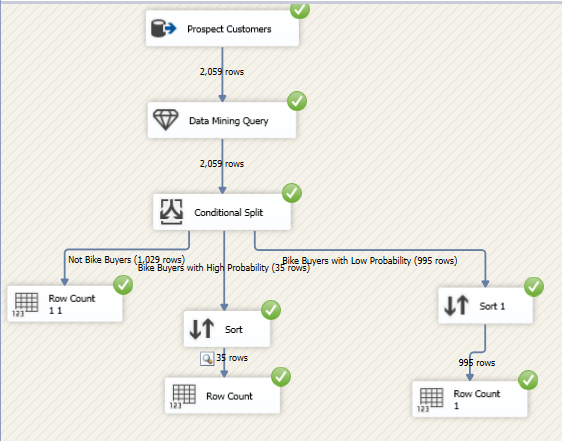
- Conditional Split Transformation: Routes data to different paths based on specified conditions.
These transformations are essential for ensuring data quality and preparing data for analysis. Selecting the right transformations for your specific needs is critical for efficient SSIS data integration.
Designing an SSIS Data Integration Package
Designing an SSIS package involves several key steps:
- Define Requirements: Clearly understand the data sources, target systems, and transformation requirements.
- Plan the Control Flow: Determine the sequence of tasks to be executed.
- Design the Data Flow: Define the data sources, transformations, and destinations.
- Configure Connection Managers: Set up connections to the data sources and target systems.
- Implement Error Handling: Implement error handling mechanisms to handle unexpected errors.
- Test and Deploy: Thoroughly test the package before deploying it to a production environment.
Proper planning and design are crucial for creating robust and maintainable SSIS packages. Consider using a modular approach, breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable components.
Best Practices for SSIS Data Integration
Following best practices can significantly improve the performance, reliability, and maintainability of your SSIS solutions. Here are some key recommendations:
- Optimize Data Flow: Minimize the number of transformations and use efficient transformations.
- Use Appropriate Data Types: Choose the appropriate data types to minimize storage space and improve performance.
- Implement Error Handling: Implement robust error handling mechanisms to handle unexpected errors gracefully.
- Use Logging: Enable logging to track the execution of the package and identify potential issues.
- Parameterize Connections: Use parameters to store connection information, making it easier to deploy the package to different environments.
- Secure Sensitive Data: Protect sensitive data by encrypting connection strings and using secure authentication methods.
- Incremental Load: Instead of loading the entire data every time, load only the changes. This significantly reduces processing time.
Adhering to these best practices will help you build high-quality SSIS data integration solutions that meet your business requirements. [See also: SSIS Performance Tuning Tips]
Advanced SSIS Data Integration Techniques
Beyond the basics, SSIS offers advanced features for handling complex data integration scenarios:
- Script Task: Allows you to write custom code in C# or VB.NET to perform complex transformations or operations.
- Web Service Task: Enables you to interact with web services.
- Event Handlers: Allow you to respond to events that occur during package execution, such as errors or warnings.
- Package Configurations: Provide a way to externalize configuration settings, making it easier to deploy the package to different environments.
These advanced techniques provide greater flexibility and control over your SSIS data integration workflows. Understanding when and how to use these features can significantly enhance your SSIS development capabilities.
Troubleshooting Common SSIS Data Integration Issues
Even with careful planning and design, you may encounter issues when developing and deploying SSIS packages. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Connection Errors: Verify the connection string and ensure that the database server is accessible.
- Data Type Mismatches: Ensure that the data types of the source and destination columns are compatible.
- Performance Issues: Optimize the data flow and use appropriate data types. [See also: Optimizing SSIS Data Flow Performance]
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling mechanisms to handle unexpected errors gracefully.
Effective troubleshooting involves analyzing error messages, reviewing logs, and using debugging tools to identify the root cause of the problem. A systematic approach to troubleshooting can help you resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
SSIS Data Integration in the Cloud
With the rise of cloud computing, SSIS is increasingly being used to integrate data in the cloud. Azure Data Factory (ADF) provides a cloud-based ETL service that is compatible with SSIS. You can migrate your existing SSIS packages to ADF and run them in the cloud. This offers several benefits, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of management. [See also: Migrating SSIS Packages to Azure Data Factory]
Using SSIS data capabilities in the cloud enables organizations to leverage the power of cloud computing for their data integration needs. This allows them to build scalable and cost-effective data integration solutions that can handle large volumes of data.
The Future of SSIS Data Integration
SSIS continues to evolve as Microsoft invests in new features and capabilities. The integration with Azure Data Factory is a key focus, enabling organizations to leverage the power of the cloud for their data integration needs. SSIS data integration remains a critical skill for data professionals, and its importance will only continue to grow as organizations increasingly rely on data to drive business decisions.
In conclusion, mastering SSIS data integration is essential for any data professional looking to build robust and scalable ETL solutions. By understanding the core concepts, key components, and best practices, you can design and deploy SSIS packages that meet your business requirements and drive better business intelligence. The future of SSIS looks bright, with continued integration with cloud technologies and ongoing investment from Microsoft.
