Unlocking Emotional Intelligence: A Deep Dive into the Feelings Wheel
In today’s fast-paced and often emotionally charged world, understanding and managing our emotions is more crucial than ever. Emotional intelligence (EQ), the ability to perceive, use, understand, manage, and handle emotions, plays a vital role in our personal and professional lives. One powerful tool that can significantly enhance our emotional literacy is the feelings wheel. This comprehensive guide will explore the feelings wheel, its origins, how to use it effectively, and its benefits for improving emotional well-being.
What is a Feelings Wheel?
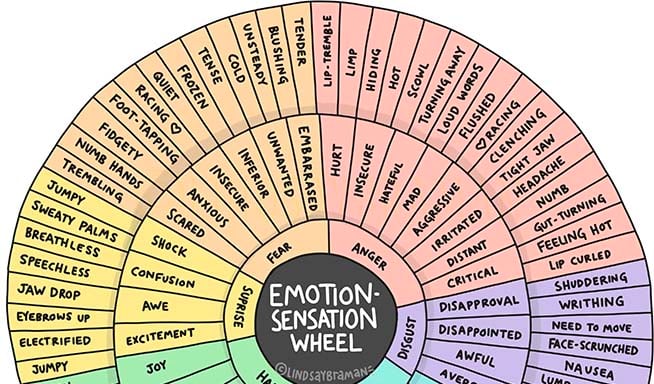
A feelings wheel, also known as an emotion wheel, is a visual tool that organizes and categorizes emotions. It typically consists of concentric circles, with core emotions at the center and more nuanced feelings radiating outwards. By presenting emotions in a structured format, the feelings wheel helps individuals identify and articulate their feelings with greater precision. It acts as a visual thesaurus for emotions, expanding our emotional vocabulary and fostering self-awareness.
The History and Development of the Feelings Wheel
While the concept of categorizing emotions dates back centuries, the modern feelings wheel is often attributed to Dr. Gloria Willcox’s “The Feeling Wheel,” published in 1982. This early version laid the groundwork for subsequent iterations. Another notable contribution came from Dr. Robert Plutchik, who developed the “Wheel of Emotions” as part of his psychoevolutionary theory of emotion. Plutchik’s wheel featured eight basic emotions arranged in opposing pairs, such as joy versus sadness and anger versus fear. These foundational works have inspired numerous variations of the feelings wheel, each tailored to different contexts and audiences. Today, you can find feelings wheel variations designed for children, therapists, and even specific professional fields.
How to Use a Feelings Wheel Effectively
Using a feelings wheel is a straightforward process that can be easily integrated into your daily routine or therapeutic practices. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Primary Emotion: Start by focusing on the core emotions at the center of the wheel. These typically include basic feelings like happiness, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, and disgust. Which of these emotions most closely aligns with what you’re experiencing?
- Explore the Secondary Emotions: Once you’ve identified the primary emotion, move outward to the next layer of the wheel. This layer contains more specific feelings related to the primary emotion. For example, if you’re feeling angry, you might explore whether you’re also feeling frustrated, irritated, or resentful.
- Pinpoint the Nuanced Emotion: Continue moving outward to the outer layers of the wheel. These layers offer even more nuanced and descriptive terms for your emotions. This step allows you to fine-tune your understanding of exactly what you’re feeling. For example, instead of just saying you’re “sad,” you might realize you’re feeling “lonely,” “disappointed,” or “grief-stricken.”
- Reflect on the Emotion: Once you’ve identified the specific emotion, take some time to reflect on it. Ask yourself why you’re feeling this way and what might be contributing to these feelings. Understanding the root cause of your emotions is crucial for managing them effectively.
- Take Action (If Necessary): Depending on the emotion you’re feeling, you may need to take action to address it. For example, if you’re feeling anxious, you might practice relaxation techniques or seek support from a friend or therapist. If you’re feeling joyful, you might want to share your happiness with others or engage in activities that bring you pleasure.
Example Scenario
Let’s say you’ve just received some unexpected negative feedback at work. Initially, you might identify your primary emotion as “anger.” Using the feelings wheel, you delve deeper and discover that you’re also feeling “frustrated” because you feel your efforts aren’t being recognized. Further exploration reveals that you’re also feeling “insecure” about your performance. Recognizing these specific emotions allows you to address the underlying issues more effectively. You might decide to schedule a meeting with your supervisor to discuss the feedback and seek clarification, or you might focus on improving your skills in the areas identified in the feedback. This process of emotional identification and action is facilitated by the feelings wheel.
Benefits of Using the Feelings Wheel
The feelings wheel offers a multitude of benefits for individuals seeking to improve their emotional intelligence and overall well-being:
- Enhanced Emotional Vocabulary: By providing a wide range of emotion words, the feelings wheel expands your emotional vocabulary, allowing you to articulate your feelings with greater precision.
- Increased Self-Awareness: The feelings wheel encourages introspection and self-reflection, leading to a deeper understanding of your emotional landscape.
- Improved Communication: Being able to accurately identify and express your feelings improves communication in your personal and professional relationships.
- Better Emotional Regulation: Understanding your emotions is the first step towards managing them effectively. The feelings wheel empowers you to regulate your emotions in a healthy and constructive manner.
- Reduced Stress and Anxiety: By identifying and addressing the root causes of your emotions, the feelings wheel can help reduce stress and anxiety levels.
- Improved Mental Health: Regular use of the feelings wheel can contribute to improved mental health by fostering emotional awareness and resilience.
Different Types of Feelings Wheels
While the basic structure of the feelings wheel remains consistent, there are several variations designed to cater to specific needs and populations:
- Basic Feelings Wheel: This is the most common type of feelings wheel, featuring a core set of emotions and expanding outward to more nuanced feelings.
- Feelings Wheel for Children: These wheels use simplified language and illustrations to help children identify and understand their emotions.
- Feelings Wheel for Therapists: These wheels are designed to assist therapists in helping their clients explore and articulate their emotions. They often include more complex and nuanced emotion words.
- Feelings Wheel for Specific Situations: Some feelings wheels are tailored to specific situations, such as grief, trauma, or addiction.
Integrating the Feelings Wheel into Daily Life
The feelings wheel is not just a tool for therapy; it can be seamlessly integrated into your daily life to enhance your emotional well-being. Here are some practical ways to incorporate the feelings wheel into your routine:
- Morning Check-In: Start your day by spending a few minutes reflecting on how you’re feeling. Use the feelings wheel to identify and articulate your emotions.
- Journaling: Use the feelings wheel as a prompt for journaling. Write about the emotions you’re experiencing and explore the reasons behind them.
- Conflict Resolution: When you’re in a conflict situation, use the feelings wheel to identify your own emotions and the emotions of the other person involved. This can help you communicate more effectively and resolve the conflict more constructively.
- Mindfulness Practice: Incorporate the feelings wheel into your mindfulness practice. As you meditate, pay attention to the emotions that arise and use the wheel to label and understand them.
- Therapy Sessions: Use the feelings wheel as a tool to communicate your emotions to your therapist. This can help them gain a deeper understanding of your emotional state and tailor their treatment accordingly.
Criticisms and Limitations
While the feelings wheel is a valuable tool, it’s essential to acknowledge its limitations. Some critics argue that the wheel oversimplifies the complexity of human emotions and that it may not accurately capture the nuances of individual experiences. Additionally, the feelings wheel is a Western-centric tool, and its categories may not be universally applicable across different cultures. It’s also important to remember that the feelings wheel is just one tool among many, and it should be used in conjunction with other strategies for emotional well-being. [See also: Mindfulness for Emotional Regulation]
Conclusion
The feelings wheel is a powerful tool for unlocking emotional intelligence. By providing a structured framework for identifying and articulating emotions, it empowers individuals to gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their emotional landscape. Whether you’re seeking to improve your communication skills, reduce stress, or enhance your overall well-being, the feelings wheel can be a valuable asset on your journey towards emotional mastery. Embrace this tool, explore its nuances, and unlock the potential for a more emotionally intelligent and fulfilling life. The ability to understand and name your feelings is a crucial step in managing them effectively and building stronger relationships with yourself and others. Start exploring the feelings wheel today and embark on a journey of emotional discovery. Remember, emotional intelligence is a skill that can be developed and refined over time, and the feelings wheel is a valuable tool to support that growth.
