Unlocking Emotions: Understanding Anger and the Secondary Emotion Wheel
Anger. It’s a powerful and often misunderstood emotion. While frequently perceived as a primary feeling, anger often masks deeper, more vulnerable emotions. The anger secondary emotion wheel serves as a valuable tool for dissecting this complex feeling, helping us identify the underlying emotions that fuel our outbursts and reactions. Understanding the subtleties of anger and its connection to the secondary emotion wheel is crucial for emotional intelligence, healthy communication, and overall well-being. This article will delve into the intricacies of anger, explore the concept of secondary emotions, and demonstrate how the anger secondary emotion wheel can be used to navigate our emotional landscape more effectively.
What is Anger? A Closer Look
Anger is a natural human emotion characterized by feelings of annoyance, frustration, or outrage. It can range from mild irritation to intense fury. While anger itself isn’t inherently negative, the way we express and manage it can have significant consequences on our relationships, work life, and personal health. It’s important to recognize that anger often serves as a protective mechanism, a signal that something feels wrong or unjust. However, understanding the root causes of our anger is essential for responding in a constructive manner.
From a physiological perspective, anger triggers a cascade of hormonal and neurological changes. Our heart rate and blood pressure increase, adrenaline surges, and our senses become heightened. This “fight-or-flight” response prepares us to confront a perceived threat. While this response was crucial for survival in our evolutionary past, it can be detrimental in modern social situations if not managed effectively.
The Concept of Secondary Emotions
This is where the concept of secondary emotions becomes critical. Secondary emotions are those that we experience as a result of a primary emotion. In the case of anger, it frequently acts as a shield, masking more vulnerable feelings such as fear, sadness, shame, or hurt. For example, someone might express anger when they feel rejected, inadequate, or powerless. By understanding that anger is often a secondary emotion, we can begin to explore the underlying causes and address the root of the problem.
Consider a scenario where a person lashes out in anger after receiving critical feedback at work. While the immediate reaction is anger, the underlying emotions might be feelings of inadequacy, fear of failure, or shame about not meeting expectations. By recognizing these secondary emotions, the individual can begin to address the core issues and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Introducing the Anger Secondary Emotion Wheel
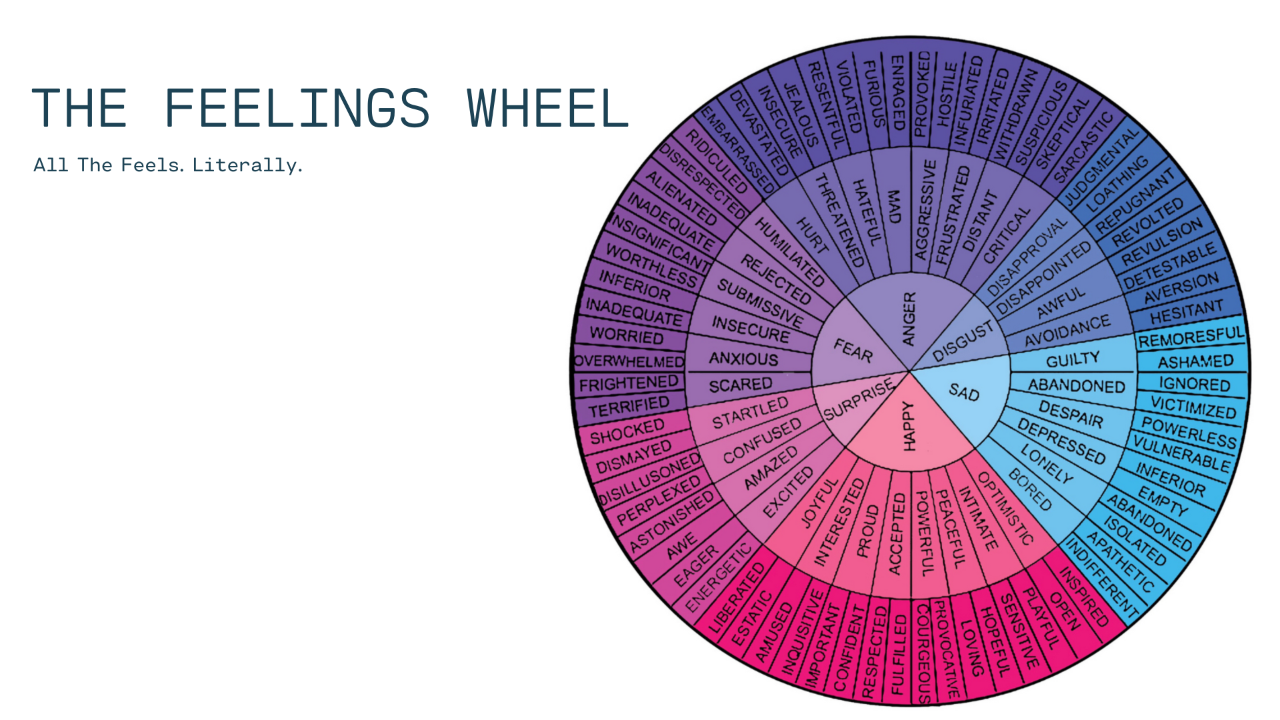
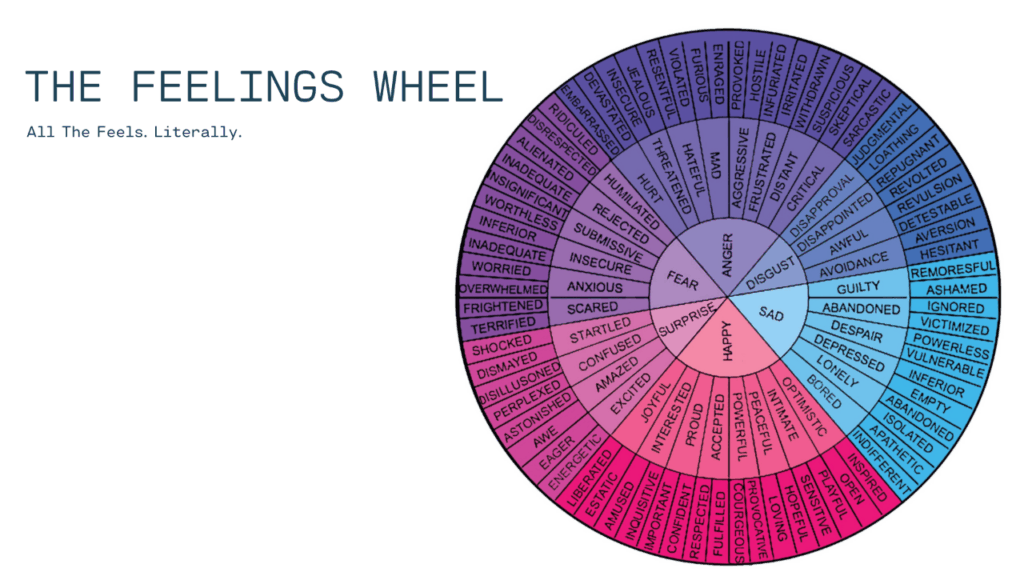
The anger secondary emotion wheel is a visual tool designed to help individuals identify the emotions that lie beneath their anger. It typically consists of a circle divided into segments, with anger at the center. Radiating outward are various secondary emotions that commonly trigger or accompany anger. These might include:
- Fear: Anxiety, insecurity, vulnerability
- Sadness: Grief, disappointment, loneliness
- Hurt: Betrayal, rejection, abandonment
- Shame: Guilt, embarrassment, humiliation
- Frustration: Annoyance, impatience, helplessness
The anger secondary emotion wheel serves as a roadmap for emotional exploration, guiding individuals to identify the specific emotions that are contributing to their anger. By pinpointing these underlying feelings, people can develop a deeper understanding of themselves and their emotional responses.
How to Use the Anger Secondary Emotion Wheel
Using the anger secondary emotion wheel is a straightforward process that involves self-reflection and emotional awareness. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Acknowledge your anger: The first step is to recognize that you are feeling angry. Pay attention to the physical sensations and thoughts associated with your anger.
- Consult the wheel: Look at the anger secondary emotion wheel and consider the emotions listed. Which ones resonate with you in this particular situation?
- Identify the underlying emotions: Ask yourself what specific events or situations might have triggered these underlying emotions. Be honest with yourself and avoid blaming others.
- Explore the root causes: Once you’ve identified the underlying emotions, delve deeper into the root causes. What past experiences or beliefs might be contributing to these feelings?
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Once you understand the underlying emotions and their root causes, you can begin to develop healthy coping mechanisms. This might involve practicing mindfulness, engaging in relaxation techniques, seeking therapy, or communicating your needs effectively.
Benefits of Using the Anger Secondary Emotion Wheel
Using the anger secondary emotion wheel offers several significant benefits:
- Increased self-awareness: It promotes a deeper understanding of your emotions and triggers.
- Improved emotional regulation: It helps you manage your anger in a more constructive way.
- Enhanced communication: It allows you to express your needs and feelings more effectively.
- Stronger relationships: It fosters empathy and understanding in your relationships.
- Reduced stress and anxiety: It helps you cope with stressful situations more effectively.
- Personal growth: Facilitates a journey of self-discovery and emotional maturity.
Examples of Using the Anger Secondary Emotion Wheel
Let’s explore a few examples of how the anger secondary emotion wheel can be applied in real-life situations:
- Scenario 1: A person becomes angry when their partner forgets their anniversary. Using the wheel, they might realize that their anger stems from feelings of hurt and rejection. They can then communicate these feelings to their partner in a calm and constructive manner.
- Scenario 2: A person becomes angry when they are passed over for a promotion at work. Using the wheel, they might realize that their anger stems from feelings of inadequacy and fear of failure. They can then focus on developing their skills and seeking opportunities for growth.
- Scenario 3: A parent becomes angry when their child misbehaves. Using the wheel, they might realize that their anger stems from feelings of frustration and helplessness. They can then explore more effective parenting strategies and seek support from other parents.
Limitations and Considerations
While the anger secondary emotion wheel is a valuable tool, it’s important to acknowledge its limitations. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, and it may not capture the full complexity of every individual’s emotional experience. Additionally, it’s essential to consider cultural and contextual factors that may influence the expression and interpretation of anger. Seeking professional guidance from a therapist or counselor can provide further support and personalized strategies for managing anger effectively. [See also: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Techniques for Anger Management]
Beyond the Wheel: Long-Term Strategies for Managing Anger
While the anger secondary emotion wheel provides immediate insight, long-term anger management requires consistent effort and the development of healthy coping mechanisms. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Mindfulness and meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help you become more aware of your thoughts and emotions in the present moment. Meditation can promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.
- Cognitive restructuring: This involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns that contribute to anger. Replace negative thoughts with more positive and realistic ones.
- Assertiveness training: Learning to communicate your needs and feelings assertively can help you avoid bottling up anger.
- Stress management techniques: Engage in activities that help you relax and de-stress, such as exercise, spending time in nature, or pursuing hobbies.
- Therapy: Working with a therapist can provide valuable support and guidance in managing anger and addressing underlying emotional issues.
Understanding and managing anger is a lifelong journey. By utilizing tools like the anger secondary emotion wheel and incorporating healthy coping mechanisms into your daily life, you can cultivate emotional intelligence, improve your relationships, and enhance your overall well-being. The key is to be patient with yourself, practice self-compassion, and seek support when needed. Recognizing that anger is often a symptom of deeper emotional wounds is the first step towards healing and growth. Embrace the anger secondary emotion wheel as a guide, and embark on a path towards emotional mastery. Remember, understanding your anger and its root causes empowers you to respond with intention, rather than react with impulse. The journey to emotional regulation starts with acknowledging the role of the anger secondary emotion wheel in unlocking your true feelings. By understanding the anger secondary emotion wheel, you gain valuable insights into your emotional landscape. Using the anger secondary emotion wheel is a proactive step toward emotional wellness.
Conclusion
The anger secondary emotion wheel is a powerful tool for understanding the complex emotions that underlie anger. By identifying these secondary emotions, individuals can gain valuable insights into their triggers, develop healthier coping mechanisms, and improve their overall emotional well-being. While it’s not a panacea, the wheel offers a practical and accessible framework for navigating the often-turbulent waters of anger. Remember to combine the use of the wheel with long-term strategies such as mindfulness, cognitive restructuring, and professional support to create lasting positive change.