Unveiling the Reasons for Milia: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Milia, those small, white, cyst-like bumps that commonly appear on the face, can be a source of cosmetic concern for many. While generally harmless, understanding the reasons for milia is crucial for both prevention and effective treatment. This article delves into the various factors that contribute to the formation of milia, exploring everything from skin conditions to lifestyle choices. We’ll also cover practical strategies for preventing these pesky bumps and the treatment options available to help you achieve clear, healthy skin.
What Exactly is Milia?
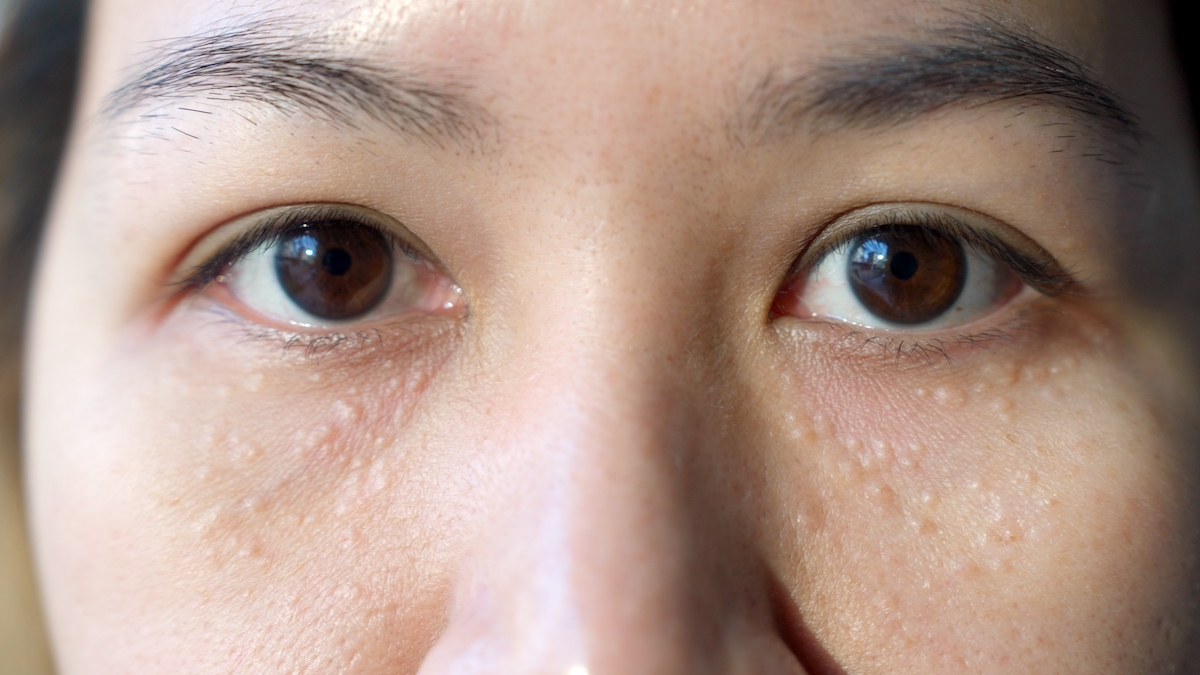
Before exploring the reasons for milia, it’s important to understand what they are. Milia are small, raised, pearly-white or yellowish bumps on the skin. They are technically epidermal cysts filled with keratin, a protein found in skin, hair, and nails. Milia are most commonly found on the face, particularly around the eyes, nose, and cheeks, but they can appear anywhere on the body. They are not painful or itchy, but some people may find them aesthetically unappealing.
Primary Milia: The Most Common Culprit
One of the main reasons for milia is primary milia. This type of milia occurs spontaneously and is not associated with any underlying skin condition or trauma. It’s believed to form when dead skin cells become trapped beneath the surface of the skin. This is more common in infants, where it often resolves on its own within a few weeks. However, primary milia can also occur in adults. Factors that contribute to primary milia include:
- Sun Damage: Prolonged sun exposure can damage the skin and make it more difficult for dead skin cells to shed properly, increasing the likelihood of milia formation.
- Poor Exfoliation: Inadequate exfoliation allows dead skin cells to accumulate, clogging pores and potentially leading to milia.
- Thick or Oily Skin: Individuals with thicker or oilier skin may be more prone to developing milia because of the increased production of sebum and dead skin cells.
Secondary Milia: A Consequence of Skin Damage
Unlike primary milia, secondary milia develops as a result of some type of skin damage or trauma. These bumps form when the skin’s natural healing process is disrupted. Several factors can lead to secondary milia, including:
- Burns: Blisters and burns can damage the skin’s surface and disrupt the normal shedding process, resulting in milia.
- Rashes and Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as eczema, rosacea, and allergic contact dermatitis, can inflame the skin and increase the risk of milia.
- Blistering Disorders: Conditions like bullous pemphigoid, which cause blistering, can leave behind milia as the skin heals.
- Cosmetic Procedures: Aggressive skin treatments, such as dermabrasion, laser resurfacing, and chemical peels, can sometimes trigger milia formation if the skin is not properly cared for afterward.
- Certain Medications: Topical steroid creams, when used for extended periods, can thin the skin and increase the susceptibility to milia.
Milia en Plaque: A Rare but Notable Cause
Milia en plaque is a rare condition characterized by a raised, inflamed patch of skin containing numerous milia. The exact cause of milia en plaque is unknown, but it’s often associated with autoimmune disorders, genetic factors, or certain medications. It most commonly appears around the ears, eyelids, or cheeks and can be difficult to treat.
Neonatal Milia: Common in Newborns
Neonatal milia is very common in newborns, affecting up to 50% of infants. These tiny, white bumps typically appear on the face, particularly the nose, cheeks, and forehead. Neonatal milia is thought to be caused by trapped keratin and underdeveloped sweat glands. Fortunately, it is usually harmless and resolves on its own within a few weeks or months without any treatment. Parents should avoid picking or squeezing the milia, as this can lead to infection.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Milia
While genetics and skin conditions play a role, certain lifestyle factors can also increase your risk of developing milia. Addressing these factors can be an important step in prevention. Some contributing lifestyle factors include:
- Poor Hygiene: Not cleansing the skin properly can lead to a buildup of dead skin cells and oil, clogging pores and promoting milia formation.
- Heavy Makeup: Using heavy or comedogenic makeup can also clog pores and prevent the skin from shedding dead cells effectively.
- Sun Overexposure: As mentioned earlier, excessive sun exposure damages the skin and can interfere with the natural exfoliation process.
- Inadequate Diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can affect skin health and potentially contribute to milia.
Preventing Milia: Proactive Steps for Clear Skin
Preventing milia is often easier than treating it. By adopting a proactive skincare routine and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can significantly reduce your risk. Here are some key preventative measures:
- Gentle Cleansing: Wash your face twice daily with a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup without stripping the skin of its natural moisture.
- Regular Exfoliation: Exfoliate your skin 1-2 times per week to remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover. Use a gentle scrub, chemical exfoliant (like AHAs or BHAs), or enzyme peel. Be careful not to over-exfoliate, as this can irritate the skin.
- Sun Protection: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every day, even on cloudy days. This protects your skin from sun damage, which can contribute to milia.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Use skincare and makeup products that are labeled as non-comedogenic, meaning they won’t clog pores.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall skin health.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated from the inside out.
Treatment Options for Milia
If you already have milia, several treatment options are available. The best approach will depend on the severity and extent of the milia. Here are some common treatment methods:
- Professional Extraction: A dermatologist or trained aesthetician can safely extract milia using a sterile needle or blade to create a small opening and then gently express the contents of the cyst. This is the most effective and immediate solution.
- Topical Retinoids: Prescription-strength retinoid creams, such as tretinoin, can help to increase cell turnover and prevent the buildup of keratin. They can also help to loosen existing milia, making them easier to remove.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels containing glycolic acid or salicylic acid can exfoliate the skin and help to unclog pores. They can be effective for treating widespread milia.
- Laser Resurfacing: Laser treatments can be used to vaporize the milia and improve the overall texture of the skin. This is a more aggressive treatment option that may require some downtime.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves freezing the milia with liquid nitrogen. This causes the milia to blister and eventually fall off.
- Electrocautery: Electrocautery uses an electrical current to burn off the milia. This is another effective treatment option, but it can leave behind some scarring.
When to See a Dermatologist
While milia are generally harmless, it’s always a good idea to see a dermatologist if you’re concerned about them. A dermatologist can accurately diagnose your condition, rule out any underlying medical issues, and recommend the best course of treatment. You should also see a dermatologist if the milia are:
- Persistent and don’t resolve on their own.
- Inflamed or painful.
- Located in a sensitive area, such as around the eyes.
- Widespread or accompanied by other skin symptoms.
Understanding the reasons for milia is the first step toward preventing and treating these common skin bumps. By adopting a good skincare routine, protecting your skin from the sun, and seeking professional help when needed, you can achieve clear, healthy skin and say goodbye to milia.
Remember, patience and consistency are key when dealing with milia. It may take some time to see results, but with the right approach, you can successfully manage and prevent these frustrating bumps.
[See also: How to Prevent Acne] [See also: Understanding Sensitive Skin] [See also: The Benefits of Chemical Peels]